Test: Isomerism of coordination compounds - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Isomerism of coordination compounds
Which of the following molecule(s) is/are showing optical isomerism?
The complex that exists as a pair of enantiomers is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following pairs of structures represent facial and meridional isomers (geometrical isomers) respectively?
 and
and  are example of which type of isomerism
are example of which type of isomerism
Which of the following types of isomerism is exhibited by
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2
i. Optical
ii. Linkage
iii. Ionization
iv. Coordination
 solution?
solution?
Consider the following complexes.

Find the number of complexes will show geometrical isomerism.
Total number of geometrical isomers from the complex [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)(NH3)] is
[Co(NH3)5SO4]Br and [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 are a pair of isomers.
The complex given is

(i) non-superimposable on its mirror images
(ii) optically active
(iii) rotate plane polarised light
(iv) planar
 is six. A complex with
is six. A complex with 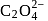 , en and superoxide
, en and superoxide  will be in the ratio to make complex
will be in the ratio to make complex 
For complex ion/compound formation reactions
(I) 
(II)  excess
excess 
(III)  gly
gly  excess
excess 
(IV)  en
en  excess
excess 
which of the following complex ion/compound does not exhibit optical activity?
 has two isomers,
has two isomers,A and
 . The solution of
. The solution of  gives a white precipitate with
gives a white precipitate with  solution and the solution of B gives white precipitate with
solution and the solution of B gives white precipitate with  solution. The type of isomerism exhibited by the complex is:
solution. The type of isomerism exhibited by the complex is:
 and
and  is :
is :
 -diamine ethane
-diamine ethane  .
.



Which of them show optical as well as geometrical isomerism?
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|


 containing one symmetrical bidentate ligand.
containing one symmetrical bidentate ligand.


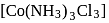 exhibits fac-mer isomerism.
exhibits fac-mer isomerism.
 and
and 
 and
and 
 complex contains elements of symmetry and is optically inactive. It does not give white precipitate with silver nitrate solution as chlorine is present in coordination sphere.
complex contains elements of symmetry and is optically inactive. It does not give white precipitate with silver nitrate solution as chlorine is present in coordination sphere.

 Each show 2 geometical isomers
Each show 2 geometical isomers
 is a complex of the type
is a complex of the type  which is octahedral. Such compounds exhibit optical and geometrical isomerism both.
which is octahedral. Such compounds exhibit optical and geometrical isomerism both.
 can
can
 exhibits
exhibits group which may be in the form
group which may be in the form  or -ONO.
or -ONO. 




 is 6
is 6 en are bidentate ligands while
en are bidentate ligands while  is unidentate
is unidentate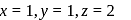

 with DMG (dimethylglyoxime) form square planar complex which is obtically inactive. While
with DMG (dimethylglyoxime) form square planar complex which is obtically inactive. While  and
and 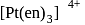 are optically active as they do not have P.O.S.
are optically active as they do not have P.O.S.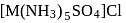 and
and 
 . They respectively give chloride ion (indicated by precipitation with
. They respectively give chloride ion (indicated by precipitation with  ) and
) and  ion (indicated by precipitation with
ion (indicated by precipitation with  ). Hence the type of isomerism exhibited by the complex is ionization isomerism.
). Hence the type of isomerism exhibited by the complex is ionization isomerism.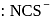 and
and 


 may exist in three isomeric form. Similarily
may exist in three isomeric form. Similarily 
 may exist in three isomeric form.
may exist in three isomeric form.
 neither G.I. nor OI
neither G.I. nor OI G. I as well as
G. I as well as 
 does not show G.I. while
does not show G.I. while














