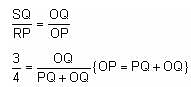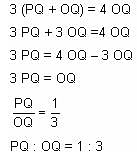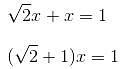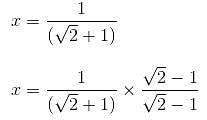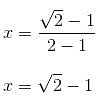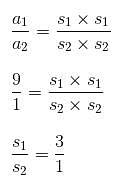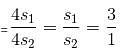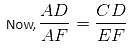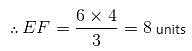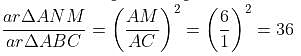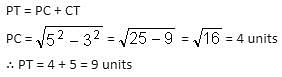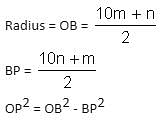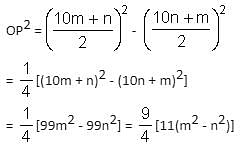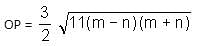Test Level 1: Geometry - 1 (September 3) - CAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for CAT Preparation - Test Level 1: Geometry - 1 (September 3)
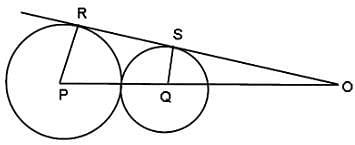
In the adjoining figure, I and II are circles with centres P and Q, respectively. The two circles touch each other and have a common tangent that touches them at points R and S, respectively. This common tangent meets the line joining P and Q at O. The diameters of I and II are in the ratio 4 : 3. It is also known that the length of PQ is 28 cm.
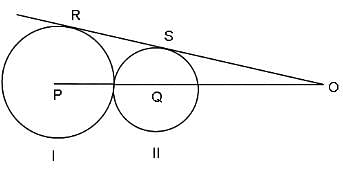
What is the ratio of the length of PQ to that of QO?

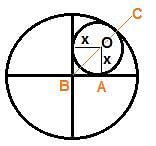
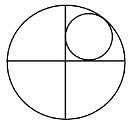
Two perpendicular lines that intersect each other at the centre of a circle of radius 1 unit divides the circle into four parts. A smaller circle is inscribed in one of those parts as shown in the figure below. What is the radius of the smaller circle?

If the ratio of areas of two squares is 9 : 1, then the ratio of their perimeters will be
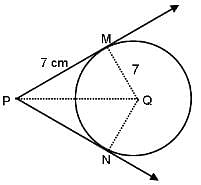
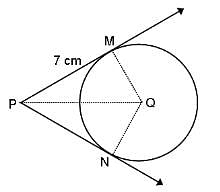
In the given figure, if PM and PN are tangents to the circle with centre Q, radius = 7 cm and PM = 7 cm, then what is the length of PQ?
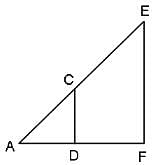
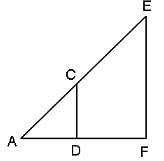
CD is parallel to EF. AD = DF, CD = 4 units and DF = 3 units. What is the measure of EF?
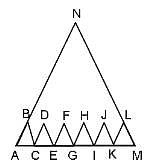
ΔABC, ΔCDE, ΔEFG, ΔGHI, ΔIJK and ΔKLM are congruent to one another and similar to ΔANM. What is the ratio of the area of ΔANM to the area of ABC?
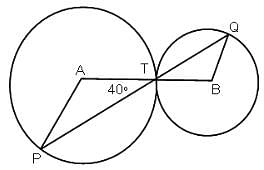
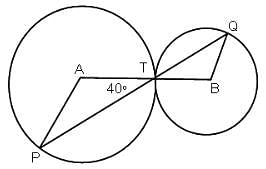
The figure given below has 2 circles with centers A and B.What is the measure of ∠APT?
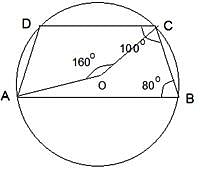
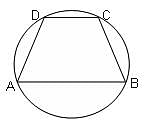
ABCD is a cyclic trapezium with segments AB and DC parallel to each other. If ∠ABC = 80°, then what is the measure of the angle subtended by major arc ABC at the centre?
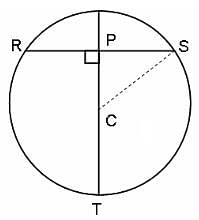
If C is the centre of the following circle, RS = 6 units and SC = 5 units, then what is the length of PT?
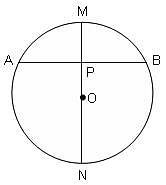
The chord AB is perpendicular to the diameter MN at P. The lengths MN and AB are two-digit integral numbers and the length AB is obtained by reversing the digits of the length MN. The length OP is a non-zero rational number. Find the diameter of the circle.
|
152 docs|327 tests
|