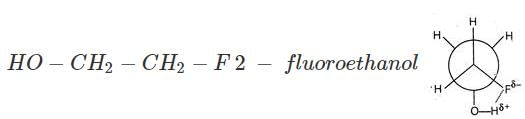Test Level 1: Previous Year Questions Isomerism - JEE MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - Test Level 1: Previous Year Questions Isomerism
Stereo - Isomerism includes -
[AIEEE - 2002]
Which of the following does not show geometrical isomerism -
[AIEEE-2002]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Racemic mixture is formed by mixing two -
[AIEEE-2002]
Geometrical isomerism is not shown by -
[AIEEE-2002]
Among the following four structures I to IV
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
It is true that -
[AIEEE-2003]
Which of the following compounds is not chiral ?
[AIEEE-2004]
Which of the following will have a mesoisomer also -
[AIEEE-2004]
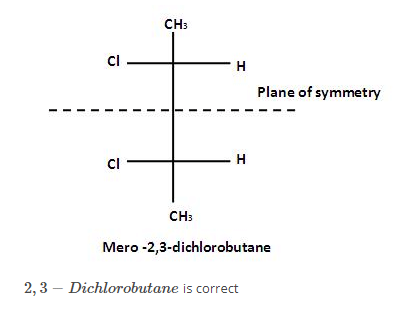
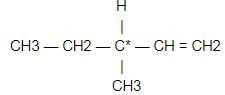
Which types of isomerism is shown by 2,3 - dichlorobutane ?
[AIEEE-2005]
Increasing order of stability among the three main conformations (i.e. Eclipse, Anti, Gauche) of 2 - fluoroethanol is
[AIEEE 2006]
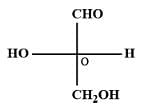
Which of the following molecules is expected to rotate the plane of plane-polarised light?
[AIEEE-2007]
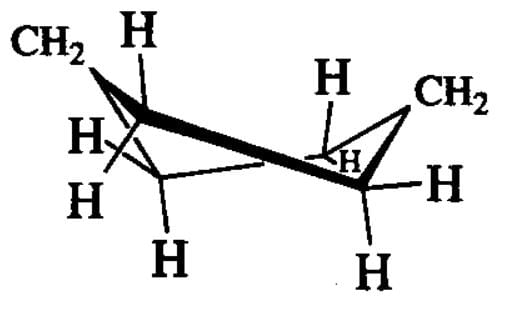
Which one of the following conformations of cyclohexane is chiral ?
[AIEEE-2007]
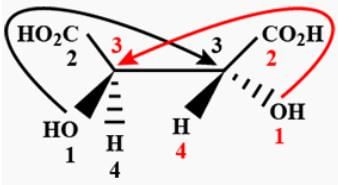
The absolute configuration of is
[AIEEE-2008]
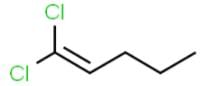
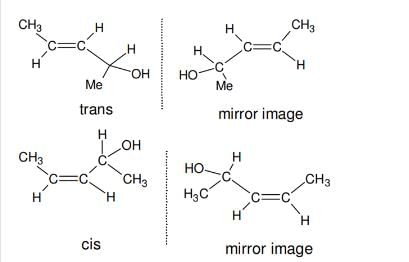
The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is :
[AIEEE-2009]
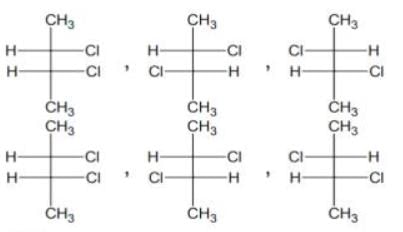
The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound of the molecular formula
CH3 - CH = CH - CH(OH) - Me is :
[AIEEE-2009]
Out of the following, the alkene that exhibits optical isomerism is
[AIEEE-2010]
How many chiral compounds are possible on monochlorination of 2 - methyl butane?
[AIEEE-2012]