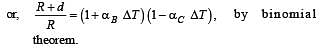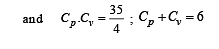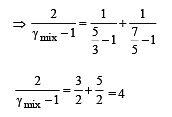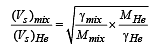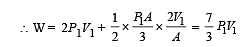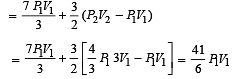Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Heat & Thermodynamics | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
26 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Heat & Thermodynamics | JEE Advanced
At room temperature, the rms speed of the molecules of a certain diatomic gas is found to be 1930 m/s. The gas is
70 calories of heat required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an ideal gas at constant pressure from 30°C to 35°C. The amount of heat required (in calories) to raise the temperature of the same gas through the same range (30°C to 35°C) at constant volume is :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Steam at 100°C is passed into 1.1 kg of water contained in a calorimeter of water equivalent 0.02 kg at 15°C till the temperature of the calorimeter and its contents rises to 80°C.
The mass of the steam condensed in kilogram is
The mass of the steam condensed in kilogram is
A cylinder of radius R made of a material of th er mal conductivity K1 is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius R and outer radius 2R made of a material of thermal conductivity K2. The two ends of the combined system are maintained at two different temperatures. There is no loss of heat across the cylindrical surface and the system is in steady state. The effective thermal conductivity of the system is
For an ideal gas :
When an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant pressure, the fraction of the heat energy supplied which increases the internal energy of the gas is
Three closed vessels A, B and C are at the same temperature T and contain gases which obey the Maxwellian distribution of velocities. Vessel A contain only O2, B only N2 and C a mixture of equal quantities of O2 and N2. If the average speed of the O2 molecules in vessel A is v1 that of the N2 molecules in vessel B is v2, the average speed of the O, molecules in vessel C is
where M is the mass of an oxygen molecule.
An ideal gas is taken from the state A (pressure P, volume V) to the state B (pressure P/2, volume 2V) along a straight line path in the P-V diagram. Select the correct statement (s) from the following:
Two bodies A and B ahave thermal emissivities of 0.01 and 0.81 respectively. The outer surface areas of the two bodies are the same. The two bodies emit total radiant power of the same rate. The wavelength λB corresponding to maximum spectral radiancy in the radiation from B shifted from the wavelenth corresponding to maximum spectral radiancy in the radiation from A, by 1.00 μm. If the temperature of A is 5802 K :
The temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 120 K to 480 K. If at 120 K the root-mean-square velocity of the gas molecules is v, at 480 K it becomes
A given quantity of a ideal gas is at pressure P and absolute temperature T. The isothermal bulk modulus of the gas is
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The piston of A is free to move, while that B is held fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B is
During the melting of a slab of ice at 273 K at atmospheric pressure,
A blackbody is at a temperature of 2880 K. The energy of radiation emitted by this object with wavelength between 499 nm and 500 nm is U1, between 999 nm and 1000 nm is U2 and between 1499 nm and 1500nm is U3. The Wien constant b = 2.88×106nm K. Then
A bimetallic strip is formed out of two identical strips one of copper and the other of brass. The coefficients of linear expansion of the two metals are αc and αB. On heating, the temperature of the strip goes up by ΔT and the strip bends to form an arc of radius of curvature R. Then R is.
Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the same ideal gas at the same temperature and the same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA, and that in B is mB. The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the same final volume 2V. The changes in the pressure in A and B are found to be ΔP and 1.5 ΔP respectively. Then
Let 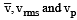 respectively denote the mean speed. root mean square speed, and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of a molecule is m. Then
respectively denote the mean speed. root mean square speed, and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of a molecule is m. Then
A vessel contains a mixture of one mole of oxygen and two moles of nitrogen at 300 K. The ratio of the average rotational kinetic energy per O2 molecule to that per N2 molecule is
A black body of temperature T is inside chamber of T0 temperature initially. Sun rays are allowed to fall from a hole in the top of chamber. If the temperature of black body (T) and chamber (T0) remains constant, then

Cv and Cp denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. Then
The figure shows the P-V plot of an ideal gas taken through a cycle ABCDA. The part ABC is a semi-circle and CDA is half of an ellipse. Then,
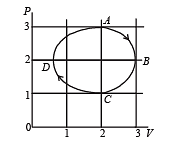
One mole of an ideal gas in initial state A undergoes a cyclic process ABCA, as shown in the figure. Its pressure at A is P0. Choose the correct option(s) from the following

A composite block is made of slabs A, B, C, D and E of different thermal conductivities (given in terms of a constant K and sizes (given in terms of length, L) as shown in the figure. All slabs are of same width. Heat ‘Q’ flows only from left to right through the blocks. Then in steady state

The figur e below sh ows th e variation of specific h eat capacity (C) of a solid as a function of temperature (T). The temperature is increased continuously from 0 to 500 K at a constant rate. Ignoring any volume change, the following statement(s) is (are) correct to a reasonable approximation..
A container of fixed volume has a mixture of one mole of hydrogen and one mole of helium in equilibrium at temperature T. Assuming the gases are ideal, the correct statement(s) is (are)
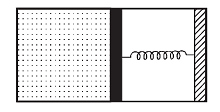
An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spring loaded piston (as shown in the figure). Initially the gas is at temperature T1, pressure P1 and volume V1 and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is then heated very slowly to temperature T2, pressure P2 and volume V2. During this process the piston moves out by a distance x. Ignoring the friction between the piston and the cylinder, the correct statement(s) is (are)
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|


















 is the value for maxima of temperatureAlso, PA VA = PB VB
is the value for maxima of temperatureAlso, PA VA = PB VB
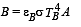






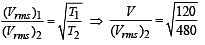




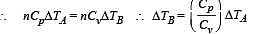







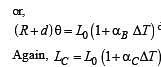
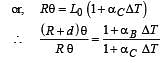 .
.