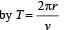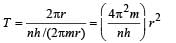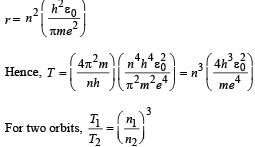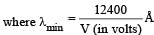Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Modern Physics | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Modern Physics | JEE Advanced
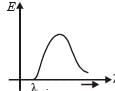
The shortest wavelength of X-rays emitted from an X-ray tube depends on
The threshold wavelength for photoelectric emission from a material is 5200 Å. Photoelectrons will be emitted when this material is illuminated with monochromatic radiation from a
From the following equations pick out the possible nuclear fusion reactions
In Bohr ’s model of the hydrogen atom
Select the correct statement from the following
For a given plate voltage, the plate current in a triode valve is maximum when the potential of
The X-ray beam coming from an X-ray tube will be
The mass number of a nucleus is
Four physical quantities are listed in Column I. Their values are listed in Column II in a random order:

The correct matching of Columns I and II is given by
Photoelectric effect suppor ts quantum nature of light because
During a negative beta decay
During a nuclear fusion reaction
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation
A freshly prepared radioactive source of half life 2 hr emits radiation of intensity which is 64 times the permissibe safe level. The minimum time after which it would be possible to work safely with this source is
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon should be doped to make a p-type semiconductor are those of
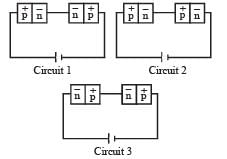
Two identical p-n junctions may be connected in series with a battery in three ways, fig. The potential drops across the two p – n junctions are equal in
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ . The halflife and mean-life of the sample are respectively given by
When a monochromatic point source of light is at a distance of 0.2 m from a photoelectric cell, the cut off voltage and the saturation current are respectively 0.6 V and 18.0 mA. If the same source is placed 0.6 m away from the photoelectric cell, then
In an n-p-n transistor circuit, the collector current is 10 mA. If 90% of the electrons emitted reach the collector,
A star initially has 1040 deuterons. It produces energy via the processes 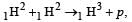 and
and 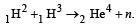 If the average power radiated by the star is 1016 W, the deuteron supply of the star is exhausted in a time of the order of
If the average power radiated by the star is 1016 W, the deuteron supply of the star is exhausted in a time of the order of
The masses of the nuclei are as follows :
M (H2) = 2.014 amu;
M (p) = 1.007 amu; M(n) = 1.008 amu; M (He4) = 4.001amu.
When photons of energy 4.25 eV strike the surface of metal A, the ejected photoelectrons have maximum kinetic energy, TA eV and de Broglie wavelength λA. The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons liberated from another metal B by photons of energy 4.70 eV is TB = (TA- 1.50) eV. If the de Broglie wavelength of these photoelectrons is λB = 2λA, then
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
Holes are charge carriers in
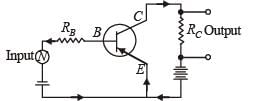
A transistor is used in the common emitter mode as an amplifier. Then
Let mp be the mass of a proton, mn the mass of a neutron, M1 the mass of a 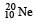 nucleus and M2 the mass of a
nucleus and M2 the mass of a 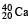 nucleus. Then
nucleus. Then
The electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition n1 → n2 where n1 and n2 are the principal quantum numbers of the two states. Assume the Bohr model to be valid. The time period of the electron in the initial state is eight times that in the final state. The possible values of n1 and n2 are
The half-life of 131I is 8 days. Given a sample of 131I at time t = 0, we can assert that
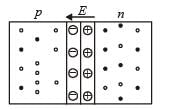
In a p-n junction diode not connected to any circuit,
X-rays are produced in an X-ray tube operating at a given accelerating voltage. The wavelength of the continuous X-rays has values from
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photoelectron emission from this substance is approximately



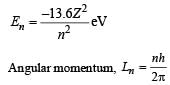
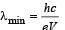
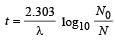
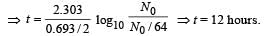
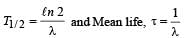

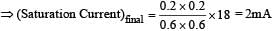
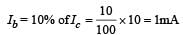
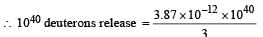
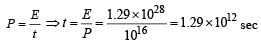
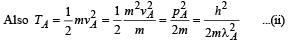
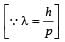
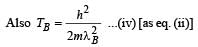
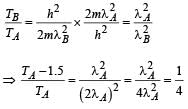
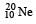 is made up of 10 protons plus 10 neutrons.
is made up of 10 protons plus 10 neutrons.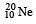 nucleus
nucleus