Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): States of Matter | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): States of Matter | JEE Advanced
When an ideal gas undergoes unrestrained expansion, no cooling occurs because the molecules : (1984 - 1 Mark)
If a gas is expanded at constant temperature :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Equal weights of ethane and hydrogen are mixed in an empty container at 25°C. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by hydrogen is (1993 - 1 Mark)
According to Graham’s law, at a given temperature the ratio of the rates of diffusion rA/rB of gases A and B is given by (1998 - 2 Marks)
(Where P and M are pressures and molecular weights of gases A and B respectively.)
5. Refer to the figure given : (2006 - 5M; –1) Which of the following statements is wrong?

A gas described by van der Waals equation – (2008- 1 Mark)
According to kinetic theory of gases (2011)
One mole of a monoatomic real gas satisfies the equation p(V – b) = RT where b is a constant. The relationship of interatomic potential V(r) and interatomic distance r for the gas is given by (JEE Adv. 2015)
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|






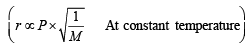
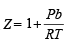 implies Z varies linearly
implies Z varies linearly . Hence, Z does not vary
. Hence, Z does not vary = nRT [For n moles of a gas)
= nRT [For n moles of a gas) represents the pressure exerted by the gas and (V– nb) the volume occupied by the gas. At low pressure, when the gas occoupies large volume the intermolecular distance between gaseous moleculas is quite large and in such case there is no significant role played by intermolecular forces and thus the gas behaves like an ideal gas thus (a) is correct NOTE : Under high pressure the intermolecular distance decreases and the intermolecular forces play a significant role and the gas shows a devation from ideal behaviour.
represents the pressure exerted by the gas and (V– nb) the volume occupied by the gas. At low pressure, when the gas occoupies large volume the intermolecular distance between gaseous moleculas is quite large and in such case there is no significant role played by intermolecular forces and thus the gas behaves like an ideal gas thus (a) is correct NOTE : Under high pressure the intermolecular distance decreases and the intermolecular forces play a significant role and the gas shows a devation from ideal behaviour.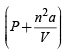 is not lower than P so (d) is
is not lower than P so (d) is
















