Test: Molecular Basis of Inheritance - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : In a DNA molecule, A–T rich parts melt before G–C rich parts.
Reason : In between A and T there are three H–bond, whereas in between G and C there are two H-bonds.
Reason : In between A and T there are three H–bond, whereas in between G and C there are two H-bonds.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The two chains of DNA have antipolarity.
Reason: In one chain of DNA, ribose sugar at 5' end consists of a free phosphate moiety while at the other end the ribose has a free 3' OH group.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Adenine cannot pair with cytosine.
Reason: Adenine and cytosine do not have a perfect match between hydrogen donor and hydrogen acceptor sites. Hence, they cannot pair.
Reason: Adenine and cytosine do not have a perfect match between hydrogen donor and hydrogen acceptor sites. Hence, they cannot pair.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The sugar phosphate backbone of two chains in DNA double helix show anti-parallel polarity.
Reason: The phosphodiester bonds in one strand go from a 3' carbon of one nucleotide to a 5' carbon of adjacent nucleotide, whereas those in complementary strand go vice versa.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: DNA is considered to be better genetic material than RNA for most organisms.
Reason: 2'-OH group present in DNA makes it labile and less reactive.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : Histones are basic proteins of major importance in packaging of eukaryotic DNA. DNA and histones comprise chromatin forming the bulk of eukaryotic chromosome.
Reason : Histones are of five major types H1,H2A H2B,H3 and H4 .
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion : DNA is associated with proteins.
Reason : DNA binds around histone proteins that form a pool and the entire structure is called a nucleosome.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Histones are basic in nature.
Reason: Histones are rich in the amino acids lysine and arginine.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: DNA acts as a genetic material in all organisms.
Reason: It is a single-stranded biomolecule.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: In Griffith's experiment, a mixture of heat-killed virulent bacteria R and live non-virulent bacteria S, lead to the death of mice.
Reason: 'Transforming principle' got transferred from heat killed R strain to S strain and made it virulent.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Template or antisense strand, having 3' → 5' polarity takes part in transcription.
Reason: Non-template or sense strand, having 5' → 3' polarity, does not take part in transcription.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The uptake of DNA during transformation is an active, energy requiring process.
Reason: Transformation occurs only in those bacteria, which possess the enzymatic machinery involved in the active uptake and recombination
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Killer strain of Paramecium aurelia can kill sensitive strain.
Reason: If sensitive strain is provided kappa particle, it becomes killer.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Scaffold proteins are nonhistone chromosomal proteins.
Reason: They are rich in lysine and arginine.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Viruses having RNA genome have shorter life span and mutate faster.
Reason: RNA is unstable and thus mutates faster.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Replication on one strand of DNA is continuous and on another is discontinuous.
Reason: The DNA polymerase works in 3' → 5' direction.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The mechanism of DNA replication is semiconservative in nature.
Reason: Each of the complementary strands of the parental double helix is conserved during the process.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Synthesis of daughter or new strand occurs continuously along the parent 3' → 5' strand.
Reason: DNA polymerase can polymerise nucleotides in 3' → 5' direction on 5' → 3' strand.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: One of the two strands of DNA is called sense strand and other is called antisense strand.
Reason: Sense strand of DNA forms complementary RNA.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The nitrogen bases of the two chains of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Reason: Both chains of DNA are antiparallel.
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|


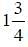 turns and twist around a histone octamer forming nucleosome. The core of
turns and twist around a histone octamer forming nucleosome. The core of














