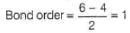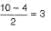Test: Molecular Orbital Theory - JEE MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Molecular Orbital Theory
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
[IIT JEE 2010]
In which of the following pairs of molecules/ions both the species are not likely to exist?
Among the following, the maximum covalent character is shown by the compound
Assuming (2s-2p) mixing is not operative, the paramagnetic species among the following is
[JEE Advanced 2014]
The common features among the species CN-, CO, NO+ and N2 are
According to MO theory which of the following lists ranks the nitrogen species in terms of increasing bond order?
Which of the following diatomic molecules would be stabilised by the removed of an electron?
Probability (electron charge density) of bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals are given.
Select the correct probability,
If one of the electrons in the He2 molecule is taken to the next excited state, then bond order in He2
If one of the electrons (1s2) of helium is taken in excited state then bond order of He2 is
The bond energy of H2 is 436 kJ mol -1. Thus, bond energy of is
Consider the following oxidation/reduction process,
Q. Magnetic moment does not change in
Direction (Q. Nos. 15) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : N2 has a greater dissociation energy than , where as O2 has lower dissociation energy than
.
Statement II : N2 has 14 electrons while O2 has 16 electrons .
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Set of species with identical bond order is/are
One of the electrons of the highest energy level is taken to next excited state in the following diatomic species. Select the species which undergoes change in bond order?
In which of the following processes, does the value of magnetic moment change ?
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-20) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Valence shell MO electronic configuration of a diatomic species is shown
* is for anti-bonding molecular orbital (MO).
Q. Bond order of this species is
Valence shell MO electronic configuration of a diatomic species is shown
* is for anti-bonding molecular orbital (MO).
Q. Divalent cation of this species
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the conversion in Column l with the type of effect given in Column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 22 and 23) This section contains 3 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Total number of electrons in anti-bonding MO in (superoxide ion) is .......
How many bonding MO are used in the formation of NO?