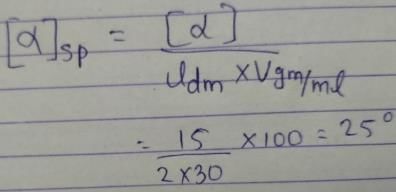Test: Optical Isomerism Polarimetry - JEE MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Optical Isomerism Polarimetry
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which is true regarding a plane polarised light?
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
At a given temperature and for a given wavelength of plane polarised light, the fundamental property of an optically active substance is
What is the percentage composition of an enantiomeric mixture of 2-butanol with a specific rotation 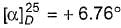 ? Specific rotation of pure enantiomer (+)-2-butanol is +13.52°.
? Specific rotation of pure enantiomer (+)-2-butanol is +13.52°.
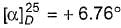 ? Specific rotation of pure enantiomer (+)-2-butanol is +13.52°.
? Specific rotation of pure enantiomer (+)-2-butanol is +13.52°.Which of the following is a comparatively significant factor affecting the magnitude of specific optical rotation?
What can be said with certainty if a compound has 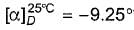 ?
?
If solution of a compound (30 g/100 mL of solution) has measured rotation of +15° in a 2 dm long sample tube, the specific rotation of this compound is
Which of the following is not true of enantiomers ? They have the same
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-12) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
Specification rotation of an optically active isomer depends on
A solution has a measured optical rotation of —24° at 25°C using D-line of sodium lamp. What can be predicted regarding this solution?
The correct statement regarding a pair of enantiomers is/are
What is/are true regarding Fischer projection of an optically active isomer?