Test: Plant Breeding (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Practice Tests: CUET Preparation - Test: Plant Breeding (Old NCERT)
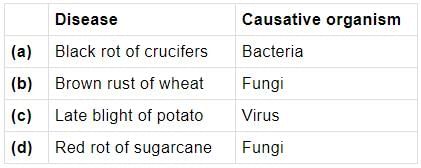
Which of the following diseases is caused by bacteria?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
First artificial hybrid was obtained by crossing sweet william and carnation, in 1717 by
Shakti Rattan and Protina (varieties of maize) are rich in
Which of the following are the species that are crossed to give sugarcane varieties with high sugar, high yield, thick stems and ability to grow in the sugarcane belt of North India?
A wheat variety, Atlas 66, which has been used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat is rich in
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding plant breeding?
Which of the following diseases is caused by virus
Maize generates resistance against stem borers by having
Which of the following statements is correct regarding nectar-less cotton varieties?
Match Column-I (crop) with Column-II (corresponding insect pests resistant variety) and select the correct option from the codes given below.

Which of the following is an example of mutation breeding?
Yellow mosaic virus resistant variety "Parbhani Kranti" belongs to
Biofortification refers to the development of crop plants which are
Consider the following three statements and select the correct option starting with which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F).
(i) Cryopreservation is one of the best methods of germplasm storage.
(ii) Hilsa, sardines and pamphlets are some freshwater fishes.
(iii) Controlled breeding experiments are carried out using artificial insemination.