Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Software Development MCQ
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2)
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) below.
Solutions of Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) | 10 questions in 12 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 1
Which section of RTE deals with the duties of teachers?
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 1
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 2
Which of the following statements about National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 2
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 3
The National Mission of SSA includes _________ of the following bodies.
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 3
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 4
The main objective of SSA is universalizing the:
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 4
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 5
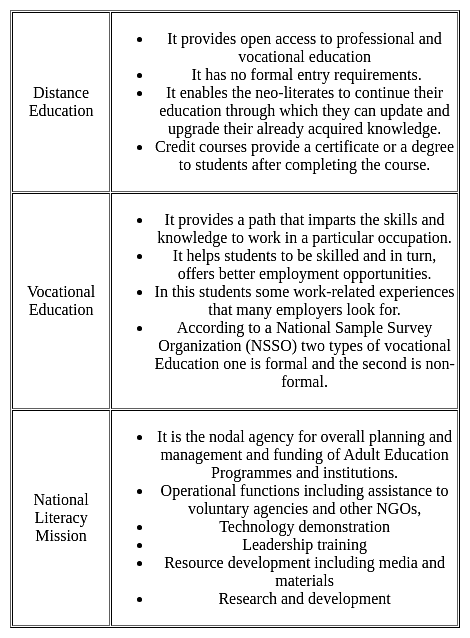
Establishment of continuing education centres, programmes of distance learning and workers’ education through the employers are the programmes included in
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 5
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 6
Which of the following made literacy a community endeavour?
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 6
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 7
Consider the following statements:
1. The target group of NLM is people between the age of 15 and 35.
2. National Literacy Mission was started by the government of India on May 1988
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 7
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 8
What is the aim of educational research?
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 8
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 9
Which of the following having the objective of Imparting of literacy skills to the all the persons economically and socially deprived sections?
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 9
Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 10
There were major shifts in learning and teaching approaches when NCF was formed. The old curriculum emphasized ________ ________ of learning but NCF 2005 emphasized ________ ________ in learning.
Detailed Solution for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) - Question 10
Information about Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Professional Knowledge (Educational Policies 2), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF