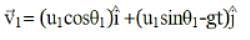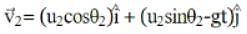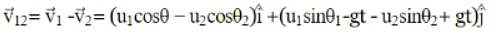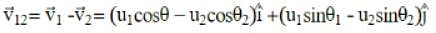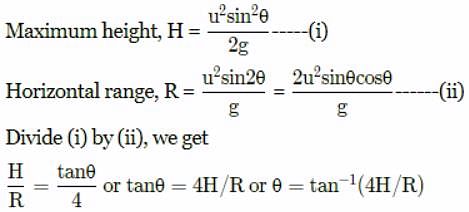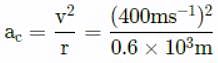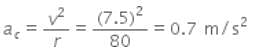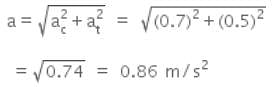Test: Projectile Motion & Uniform Circular Motion (May 20) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Projectile Motion & Uniform Circular Motion (May 20)
Which of the following is true regarding projectile motion?
In case of a projectile motion, what is the angle between the velocity and acceleration at the highest point?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two particles are projected simultaneously in the same vertical plane, from the same point, both with different speeds and at different angles with horizontal. The path followed by one, as seen by the other, is
The relation between the time of flight of projectile Tf, and the time to reach the maximum height tm is
If R and H represent horizontal range and maximum height of the projectile, then the angle of projection with the horizontal is:
What is approximately the centripetal acceleration (in units of acceleration due to gravity on earth, g = 10 m s-2) of an air-craft flying at a speed of 400 m s-1 through a circular arc of radius 0.6 km?
A body executing uniform circular motion has its position vector and acceleration vector
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
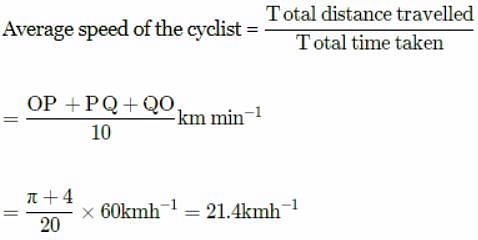
A cyclist starts from the centre O of a circular park of radius 1 km, reaches the edge P of the park, then cycles along the circumference and returns to the centre along QO as shown in the figure.
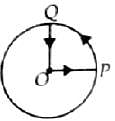
If the round trip takes ten minutes, the net displacement and average speed of the cyclist (in metre and kilometre per hour) is
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 27 km h-1. As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 80 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at the constant rate of 0.50 m s-1 every second. The net acceleration of the cyclist on the circular turn is
|
360 tests
|


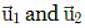 be the initial velocities of the two particles and θ1 and θ2 be their angles of projection with the horizontal.
be the initial velocities of the two particles and θ1 and θ2 be their angles of projection with the horizontal.