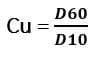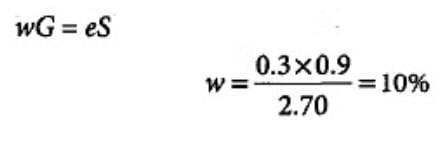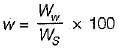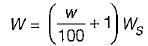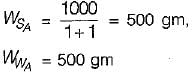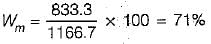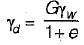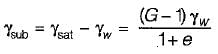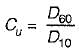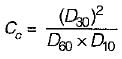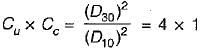Test: Properties of Soil - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Properties of Soil - 1
An undisturbed soil sample has a plastic limit of 25%, a natural moisture content of 40% and liquidity index of 50%, Its liquid limit in % will be
A well graded soil has a coefficient of curvature between
The ratio of the undisturbed shear strength to the remoulded shear strength in cohesive soil under undrained conditions is
Which of the following is a measure of particle size range?
The principle involved in the relation
γsub. = γsat - γw is
Given for a soil sample:
Degree of saturation = 90%
Specific gravity of soil grains = 2.70
Void ratio = 0.30
The water content of the sample is
For distinguishing clays from silts in the field, a moist soil is rolled into a thread of 3 mm diameter. This test will indicate the
Which one of the following is the water content of the mixed soil made from 1 kg of soil (say A) with water content of 100% and 1 kg of soil (say B) with water content of 50%?
Which one of the following gives the correct decreasing order of the densities of a soil sample?
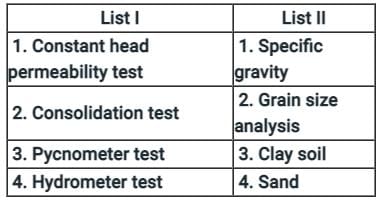
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below in the options:
For a given soil sample,
If Cc = 1.0 and Cu = 4.0, then the value of D30/D10 would be
Which of the following methods is most accurate for the determination of the water content of soil?
Valid range for S, the degree of saturation of soil in percentage is


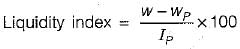
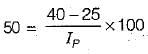

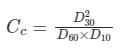
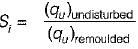
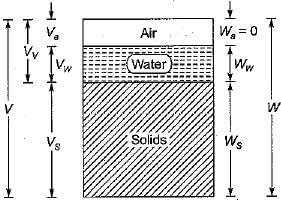

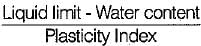 for a soil mass is called:
for a soil mass is called: