Test: Refrigeration Cycles & Systems - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Thermodynamics - Test: Refrigeration Cycles & Systems - 1
Air refrigeration cycle is generally employed in
Which is usually the costliest item in a refrigeration system?
In a vapour compression refrigeration system, a throttle valve is used in place of expander because
The bank of tubes at the back of a domestic refrigerator of vapour compression type are
For small installations of refrigeration systems (up to 35 kW), which type of condenser is used?
The pressure in a capillary tube decreases due to which of the following:
1. frictional resistance offered by the tube wall
2. acceleration of refrigerant in the tube
3. heat transfer from the tube
4. decrease in potential energy
Q. Which of the above statements are correct?
An ideal vapour compression refrigerator operates between a condenser pressure P1 and an evaporator pressure P2. Which of the following changes would increase its COP?
Which of the following parameters is made as basis of comparing different type of air- refrigeration systems?
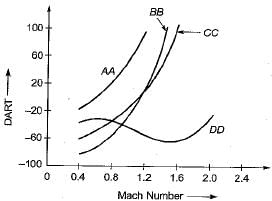
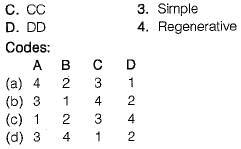
The following figure compares different aircraft refrigeration systems. Match List-I with List-ll pertaining to comparison of DART vs. Mach number variation

|
29 videos|150 docs|36 tests
|