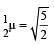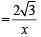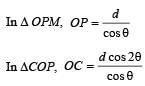Test: Single Correct MCQs: Ray & Wave Optics | JEE Advanced - ACT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Single Correct MCQs: Ray & Wave Optics | JEE Advanced
When a ray of light enters a glass slab from air,
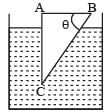
A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water (refractive index 4/3). A light beam incident normally on the face AB is totally reflected to reach on the face BC if

In Young’s double-slit experiment, the separation between the slits is halved and the distance between the slits and the screen is doubled. The fringe width is
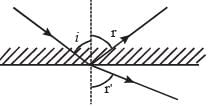
A ray of light from a denser medium strike a rarer medium at an angle of incidence i (see Fig). The reflected and refracted rays make an angle of 90° with each other. The angles of reflection and refraction are r and r’ The critical angle is
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities I and 4 I are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are
Spherical aberration in a thin lens can be reduced by
A beam of light of wave length 600 nm from a distance source falls on a single slit 1 mm wide and a resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 2m away. The distance between the first dark fringes on either side of central bright fringe is
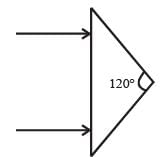
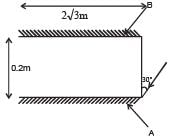
An isosceles prism of angle 120° has a refractive index 1.44. Two parallel monochromatic rays enter the prism parallel to each other in air as shown. The rays emerge from the opposite faces
A diminished image of an object is to be obtained on a screen 1.0 m from it. This can be achieved by appropriately placing
The focal lengths of the objective and the eye piece of a compound microscope are 2.0 cm and 3.0 cm, respectively.
The distance between the objective and the eye piece is 15.0 cm. The final image formed by the eye piece is at infinity.
The two lenses are thin. The distance in cm of the object and the image produced by the objective, measured from the objective lens, are respectively
Consider Fraunhoffer diffraction pattern obtained with a single slit illuminated at normal incidence. At the angular position of the first diffraction minimum the phase difference (in radians) between the wavelets from the opposite edges of the slit is
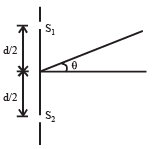
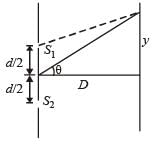
In an interference arrangement similar to Young’s doubleslit experiment, the slits S1 and S2 are illuminated with coherent microwave sources, each of frequency 106 Hz. The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference.
The slits are separated by a distance d = 150.0 m. The intensity I (θ) is measured as a function of θ, where θ is defined as shown. If I0 is the maximum intensity, then I (θ) for 0 < θ < 90° is given by
A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5 h as both surfaces of same radius of curvature R. On immersion in a medium of refractive index 1.75, it will behave as a
Yellow light is used in a single slit diffraction experiment with slit width of 0.6 mm. If yellow light is replaced by X– rays, then the observed pattern will reveal,
A thin slice is cut out of a glass cylinder along a plane parallel to its axis. The slice is placed on a flat glass plate as shown in Figure.
The observed interference fringes from this combination shall be
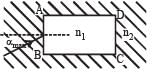
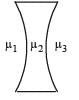
A hollow double concave lens is made of very thin transparent material. It can be filled with air or either of two liquids L1 or L2 having refractive indices μ1 and μ2 respectively (μ2 > μ1 > 1). The lens will diverge a parallel beam of light if it is filled with
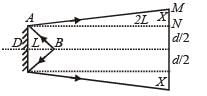
A point source of light B is placed at a distance L in front of the centre of a mirror of width 'd' hung vertically on a wall. A man walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance 2L from it as shown in fig. The greatest distance over which he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is

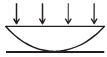
A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angle α , falls symmetrically on a glass slab as shown. The angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal. If the thickness of the glass slab is t and the refractive index n, then the divergence angle of the emergent beam is
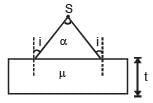
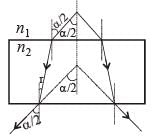
A rectangular glass slab ABCD of refractive index n1 is immersed in water of refractive index n2(n1 > n2). A ray of light is incident at the surface AB of the slab as shown. The maximum value of the angle of incidence αmax such that the ray comes out only from the other surface CD is given by
In a double slit experiment instead of taking slits of equal widths, one slit is made twice as wide as the other. Then, in the interference pattern
In a compound microscope, the intermediate image is
Two beams of light having intensities I and 4I interfere to produce a fringe pattern on a screen. The phase difference between the beams is π/2 at point A and π at point B. Then the difference between the resultant intensities at A and B is
In a Young’s double slit experiment, 12 fringes are observed to be formed in a certain segment of the screen when light of wavelength 600 nm is used. If the wavelength of light is changed to 400 nm, number of fringes observed in the same segment of the screen is given by
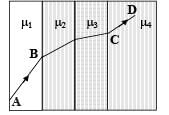
A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive indices μ1, μ2, μ3 and μ4 as shown in the figure.
The surfaces of all media are parallel. If the emergent ray CD is parallel to the incident ray AB, we must have
A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism P. Additional prism Q and R of identical shape and of the same material as P are now added as shown in the figure. The ray will now suffer
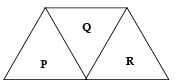
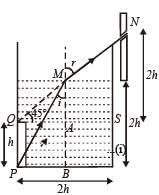
An observer can see through a pin-hole the top end of a thin rod of height h, placed as shown in the figure. The beaker height is 3h and its radius h. When the beaker is filled with a liquid up to a height 2h, he can see the lower end of the rod. Then the refractive index of the liquid is
Which one of the following spherical lenses does not exhibit dispersion? The radii of curvature of the surfaces of the lenses are as given in the diagrams.
In the ideal double-slit experiment, when a glass-plate (refractive index 1.5) of thickness t is introduced in the path of one of the interfering beams (wave-lengh t λ), the intensity at the position where the central maximum occurred previously remains unchanged. The minimum thickness of the glass-plate is
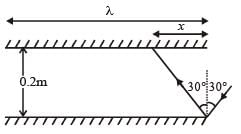
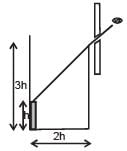
Two plane mirrors A and B are aligned parallel to each other, as shown in the figure. A light ray is incident at an angle 30° at a point just inside one end of A. The plane of incidence coincides with the plane of the figure. The maximum number of times the ray undergoes reflections (including the first one) before it emerges out is
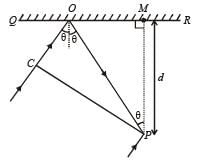
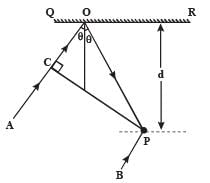
In the adjacent diagram, CP represents a wavefront and AO & BP, the corresponding two rays. Find the condition on θ for constructive interference at P between the ray BP and reflected ray OP.



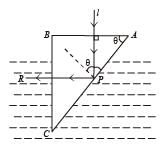
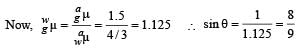 ∴ sin θ should be greater than 8/9.
∴ sin θ should be greater than 8/9.
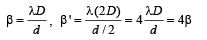
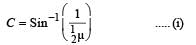
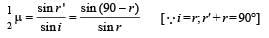
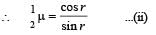
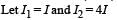
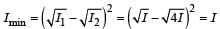
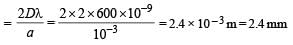
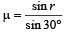
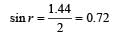
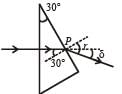
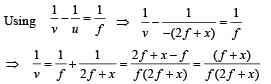
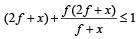
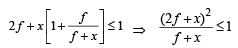 ⇒ (2f + x)2 < f + x. The above is true for f < 0.25 m.
⇒ (2f + x)2 < f + x. The above is true for f < 0.25 m.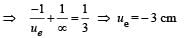
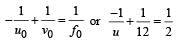
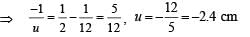
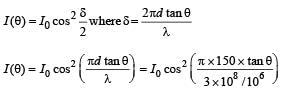
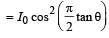
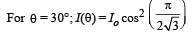
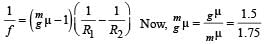 For concave lens as shown in figure in this case
For concave lens as shown in figure in this case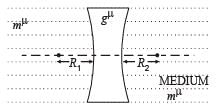
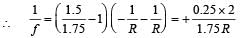
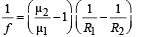
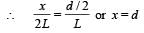
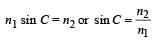
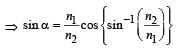
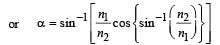
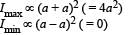
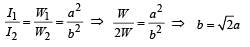
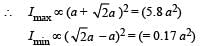
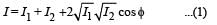
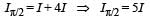
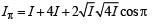
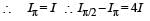
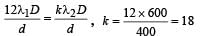
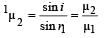 ...(1)
...(1)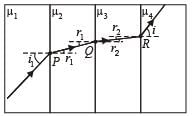
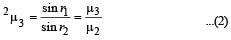

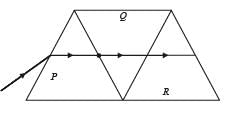
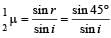
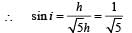 ...(ii)
...(ii)