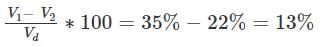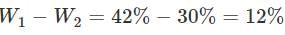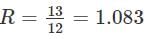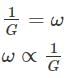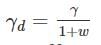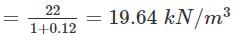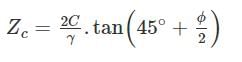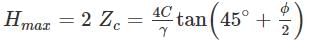Test: Soil Mechanics - SSC JE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Soil Mechanics
In Boussinesq’s solution to the problem of stress distribution, all the following assumptions are made, except:
Spring analogy in soil mechanics is used for explaining which of the following phenomenon?
The term _________ on soil is used to indicate the maximum pressure which can be exerted on soil while taking into account shear failure, settlement and the ability of structure to resist settlement.
If the coefficient of uniformity of a soil is 16 and the coefficient of curvature is 1, then what is the ratio D60/D30?
The shear test in which full consolidation occurs and excess pore pressure is build up during shearing stage is known as:
A soil mass has a void ratio of 0.67? How much water (in litres) will be required to fully saturate 1 m3 of the soil?
If the fineness modulus of sand is 3, then the sand is graded as
Find the shrinkage ration of a soil sample whose plastic limit and liquid limit values are 30% and 42%, respectively, and the values of percentage of volume change from liquid limit to dry state and plastic limit to dry state are 35% and 22%, respectively, of dry volume.
In vane shear test, the torque rod is rotated at a uniform speed of:
Which of the following shows the CORRECT order of increasing surface areas of the given soil?
What is the assumption made about back of wall, in the Rankine’s theory of earth pressure?
If in a soil mass, the product of degree of saturation (s) and void ratio (e) is 1. Then water content (ω) is
A soil has a bulk density of 22 kN/m3 and water content of 12%. The dry density of soil is
What is the ratio of discharge through the tube well to the discharge through the open well
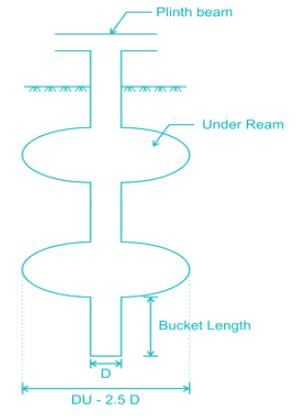
The pile provided with one or more bulbs in its vertical shaft, is generally known as
The angle of inclination of the plane at which the body begins to move down the plane, is called
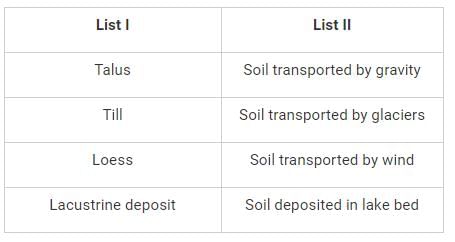
Match List I (Types of Soil) with List II (weathering agent) and select the answer option given below:-
The maximum height of an unsupported vertical cut in a cohesive soil is given by ________









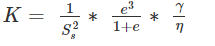
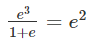
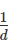
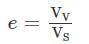
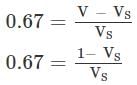
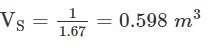
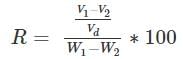
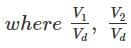 are percentage change of volume from liquid limit to dry state and plastic limit to dry state respectively
are percentage change of volume from liquid limit to dry state and plastic limit to dry state respectively