Test: Solid & Radioactive Wastes (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Practice Tests: CUET Preparation - Test: Solid & Radioactive Wastes (Old NCERT)
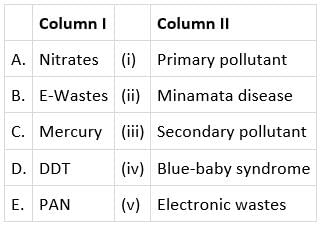
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Ahmed Khan, a plastic sack manufactturer of Bangalore, in 1998, developed polyblend, a fine powder of recycled modified plastic.
(ii) In collaboration with RV College of Engineering and Bangalore City Corporation, he proved that the mixture of polyblend and bitumen was better for road carpeting as it had better water repellent property.
(iii) By 2002, more than 40 km roads of Bangalore were laid with the help of Khan's mixture
(iv) Rag pickers who used to get 0.40 per kg of plastic waste started getting 6.00 from Ahmed Khan.
(v) INnovation like polyblend might help the modern society from being smothered with plastic waste.
(i) Ahmed Khan, a plastic sack manufactturer of Bangalore, in 1998, developed polyblend, a fine powder of recycled modified plastic.
(ii) In collaboration with RV College of Engineering and Bangalore City Corporation, he proved that the mixture of polyblend and bitumen was better for road carpeting as it had better water repellent property.
(iii) By 2002, more than 40 km roads of Bangalore were laid with the help of Khan's mixture
(iv) Rag pickers who used to get 0.40 per kg of plastic waste started getting 6.00 from Ahmed Khan.
(v) INnovation like polyblend might help the modern society from being smothered with plastic waste.
Some statements are given below each with one or two blanks. Select the option that correctly fills up the blanks.
(i) High concentration of DDT disturbs ____ in birds, which causes ____.
(ii) ____ burns more efficiently as compared to petrol and diesel.
(iii) ___ is the natural ageing of a lake which occurs due to accumulation of ____.
(iv) ______ reduces the number of organisms which are sensitive to high temperature.
(v) Irreparable computers and other electronic goods are known as ____.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Open landfilling refers to the throwing waste on an uncovered area, which is periodically burnt or compressed.
Statement 2: In sanitary landfilling, the waste is compacted and covered by layer of dirt.
Pollution from animal excreta and organic waste from kitchen can be most profitably minimized by
The effect of today's radioactive fallout will probably be more harmful to children of future generation than to present day children because
Which of the following isotopes is most dangerous to human beings?
Which of the following statements is correct?
Select the correct statement out of the following.

















