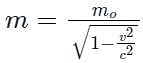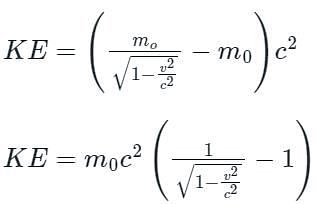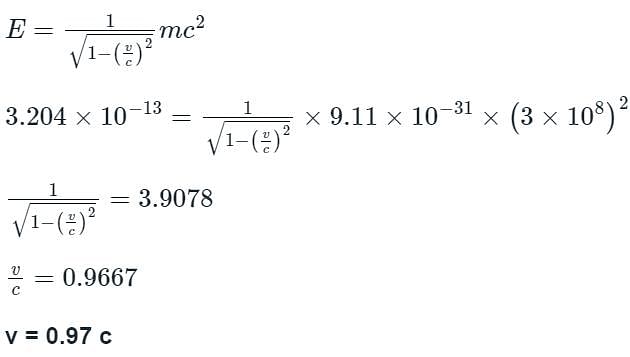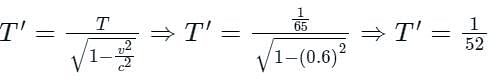Test: Special Theory of Relativity - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physics for EmSAT Achieve - Test: Special Theory of Relativity
The kinetic energy of an electron moving with a speed of 0.8c and rest mass energy of 0.321 MeV is:
On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles ________.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Light with an energy flux of 500 kW/m2 falls for 5 minutes at normal incidence on a non-reflecting circular surface with a radius of 10 cm. The total momentum delivered to this surface has a magnitude of ______.
Consider the following statements:
(a) No object can move faster than the speed of light.
(b) Space and time are relative and all motion must be relative to a frame of reference.
Which form of energy is possessed by a horse running on a level road?
What would be the momentum of the bullet and the gun before firing?
A unique idea which was considered in special theory of relativity was
The speed of a fast moving electron, having total energy of 2 MeV, is nearly:
An astronaut at rest has a heart rate of 65 beats/min. When the astronaut’s spaceship moves at a speed of 0.6 c, her heart rate as measured by an earth observer will be:
|
208 videos|230 docs|191 tests
|
|
208 videos|230 docs|191 tests
|