JEE Exam > JEE Tests > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - JEE MCQ
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - JEE MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory for JEE 2024 is part of Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced preparation. The Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory questions and answers have been
prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory below.
Solutions of Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE & Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 1
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 2
Statement Type
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : Mn(π— C3H5)(CO)4, obey effective atomic number rule.
Statement II : π-allyl ligand act as a 3e- donor.
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
*Answer can only contain numeric values
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 3
In Mn2(CO)10, the number of CO molecules in between the metal atoms are
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 3
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 4
The correct order for wavelengths of absorption in the visible region for the following complexes will be
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 4
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 5
Which will give a white precipitate with  in aqueous solution
in aqueous solution
 in aqueous solution
in aqueous solution
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 6
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 7
Amongst  and
and  , which are the colourless species?
, which are the colourless species?
(atomic number of Ti = 22, Co = 27, Cu = 29, Ni = 28)
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 7
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 8
InFe(CO)s, the Fe-C bond possesses
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 8
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 9
The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral  and tetrahedral
and tetrahedral  complexes is related as
complexes is related as
 and tetrahedral
and tetrahedral  complexes is related as
complexes is related as
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 9
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 10
Calculate the magnetic moment of  ion
ion  .
.
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 10
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 11
For octahedral complex, which of the following  configurations of metal cation cannot exist in high spin and low spin forms?
configurations of metal cation cannot exist in high spin and low spin forms?
 configurations of metal cation cannot exist in high spin and low spin forms?
configurations of metal cation cannot exist in high spin and low spin forms?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 11
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 12
Which of the following complex ions has electrons that are symmetrically filled in both  and
and  orbitals ?
orbitals ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 12
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 13
Which of the following statements related to crystal field splitting in octahedral coordination entities is incorrect?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 13
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 14
Among the following species the one which causes the highest 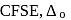 as a ligand is:
as a ligand is:
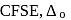 as a ligand is:
as a ligand is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 14
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 15
The increasing order of crystal field splitting strength of the given ligands is
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 16
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 17
Which of the following carbonyls will have the strongest  bond ?
bond ?
 bond ?
bond ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 17
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 18
Which of the following does not have a metal carbon bond?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 18
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 19
If the crystal field splitting energy of a tetrahedral complex  of the type
of the type  is
is  , what is the crystal field splitting energy with respect to an octahedral complex,
, what is the crystal field splitting energy with respect to an octahedral complex,  ?
?
 of the type
of the type  is
is  , what is the crystal field splitting energy with respect to an octahedral complex,
, what is the crystal field splitting energy with respect to an octahedral complex,  ?
?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 19
Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 20
The  for
for  complex is
complex is  . The
. The  for
for  will be:
will be:
 for
for  complex is
complex is  . The
. The  for
for  will be:
will be:
Detailed Solution for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory - Question 20
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Information about Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Stability of complex ion, Crystal Field Theory, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Download as PDF


 , find the value of
, find the value of 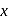 ?
? has zero oxidation state, as has zero oxidation state in the compound.
has zero oxidation state, as has zero oxidation state in the compound. is
is 
 has 6 valencies, as
has 6 valencies, as  in this state is stable due to half-filled orbitals. Now, for 6 valencies,
in this state is stable due to half-filled orbitals. Now, for 6 valencies,  is required. Therefore,
is required. Therefore,  The compound is
The compound is  .
.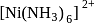 ,
, and (III)
and (III)  are made of
are made of  and ligands
and ligands  and
and  respectively. The field strength order of the ligands is
respectively. The field strength order of the ligands is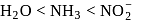
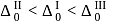
 or
or 
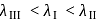



 , larger the stability
, larger the stability that exists in solution.
that exists in solution. and
and  and
and 
 metal to ligand back bonding in Fe-C bond of the organometallic compound
metal to ligand back bonding in Fe-C bond of the organometallic compound So it possesses both
So it possesses both 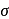 and
and  characters.
characters.


 and
and  octahedral complexes number of unpaired
octahedral complexes number of unpaired 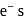 at central metal atom/ion never changes, therefore for such octahedral complexes terms high spin and low spin not used.
at central metal atom/ion never changes, therefore for such octahedral complexes terms high spin and low spin not used.
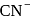 is a strong field ligand and form low spin complexes thus
is a strong field ligand and form low spin complexes thus 
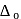 for the ligands.
for the ligands. 


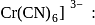 Hybridization
Hybridization  High or
High or is an example of
is an example of  system of configuration.
system of configuration. orbitals of CO ligand (donation of electron density into
orbitals of CO ligand (donation of electron density into  orbitals of
orbitals of  result in weakening of
result in weakening of 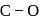 bond ). Hence, the
bond ). Hence, the 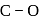 bond would be strongest in
bond would be strongest in 

 of
of  is
is  , the CFSE of octahedral complex
, the CFSE of octahedral complex 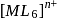 will be
will be  .
.















