Test: Surface Chemistry - Chemistry MCQ
19 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Surface Chemistry
The correct ascending order of adsorption of the following gases on the same mass of charcoal at same temperature and pressure is
Collodion is 4% solution of which one of the following in alcohol-ether mixture.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
H2 gas is adsorbed on activated charcoal to a very little extent in comparison to easily liquefiable gases due to.
The coagulation values in millimoles per litre of the electrolyte for the coagulation of As2S3 sol are given
I. NaCl (52)
II. BaCl2 (0.69)
III. MgSO4 (0.22)
The correct order of coagulating power is
3g of activated charcoal was added to 50 ml of acetic acid solution (0.06 M) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of filtrate was found to be 0.042 M. The amount of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of charcoal is
Which of the following statements are correct about solid catalyst?
Extent of adsorption of adsorbate from solution phase increases with __________
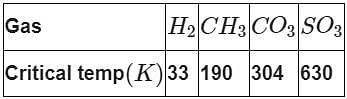
On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of
According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm, which of the following is correct?
During the adsorption of gas on the surface of solid, which of the following is true?
Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with ___________.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression xm = k p1/n which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this expression.
The best coagulant for the precipitation of Fe(OH)3 sol is
|
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|

















