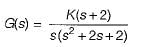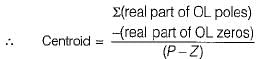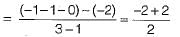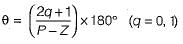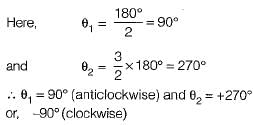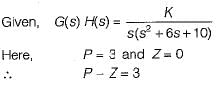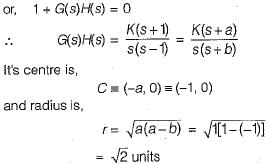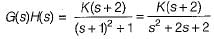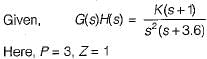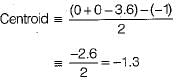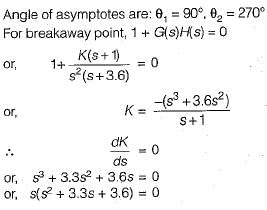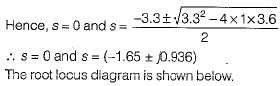Test: The Root Locus Technique - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: The Root Locus Technique - 1
Which of the following option is correct?
The root locus is the path of the roots of the characteristic equation traced out in the s-plane
The root locus is the path of the roots of the characteristic equation traced out in the s-plane
Number of intersection of the asymptotes of the complete root loci is
The open-loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is given by:
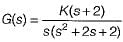
The centroid and the angle of root locus asymptotes are respectively
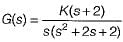
The centroid and the angle of root locus asymptotes are respectively
Consider the loop transfer function K(s + 6) / (s + 3)(s +5 ) In the root locus diagram the centroid will be located at:
Assertion (A): Root locus is a graphical method in which roots of the characteristic equation are plotted in s-plane for the different value of parameter.
Reason (R): The locus of the roots of the characteristic equation when gain is varied from zero to infinity is called root locus.
Assertion ( A ) : An addition of real pole at s = - p0 in the transfer function G(s)H(s) of a control system results in the increase of stability margin.
Reason ( R ) : An addition of real pole at s = - p0 in the transfer function G(s)H(s) will make the resultant root loci bend towards the right.
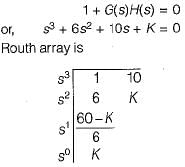
The open-loop transfer function of a closed loop control system is given as:
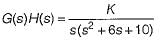
Which of the following statements is correct about the root locus of the above system?
The root locus of s(s - 1) + K(s + 1) = 0 is a circle. The co-ordinates of the centre and the radius (in units) of this circle are respectively
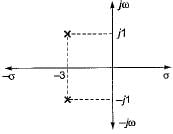
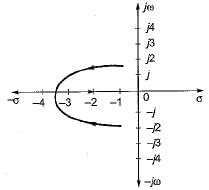
What is the open-loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system having root locus shown in the following figure?
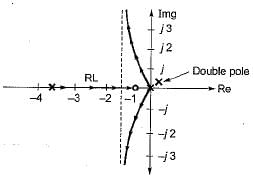
A control system has G(s)H(s) 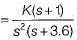 (0 < K < ∞). The number of breakaway point in the root locus diagram is/are
(0 < K < ∞). The number of breakaway point in the root locus diagram is/are
|
26 docs|257 tests
|
|
26 docs|257 tests
|