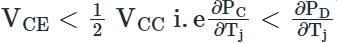Test: Thermal Runaway & Thermal Stability - UPSC MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermal Runaway & Thermal Stability
For a given transistor, the thermal resistance is 8°C/W and for the ambient temperature TAis 27°C. If the transistor dissipates 3W of power, calculate the junction temperature (TJ).
A silicon power transistor is operated with a heat sink HS-A=1.5°C/W. The transistor rated at 150W (25°C) has HJ-C=0.5°C/W and the mounting insulation has HC-S=0.6°C/W. What maximum power can be dissipated if the ambient temperature is 40°C and (TJ)MAX=200°C?
The total thermal resistance of a power transistor and heat sink is 20°C/W. The ambient temperature is 25°C and (TJ)MAX=200°C. If VCE=4V, find the maximum collector current that the transistor can carry without destruction. What will be the allowed value of collector current if ambient temperature rises to 75°C?
The condition to be satisfied to prevent thermal runaway?
Thermal stability can be obtained by_________
Thermal stability is dependent on thermal runaway which is_________
When the temperature is increased, what happens to the collector current after a feedback is given?
When the temperature is increased, what happens to the collector current after a feedback is given?
Discrete transistors T1 and T2 having maximum collector current rating of 0.75A are connected in parallel as shown in the figure. This combination is treated as a single transistor to carry a single current of 1A, when biased with a self bias circuit. When the circuit is switched ON, T1 had draws 0.55A and T2 draws 0.45A. If the supply is kept ON continuously, it is very likely that_________
When the collector current is increased in a transistor_________
When the power dissipation increases in a transistor, the thermal resistance_________
Which of the following biasing techniques are prone to thermal runaway?
For a given transistor, the thermal resistance is 8°C/W and for the ambient temperature TA is 27°C. If the transistor dissipates 3W of power, calculate the junction temperature (TJ).
The total thermal resistance of a power transistor and heat sink is 20°C/W. The ambient temperature is 25°C and (TJ)MAX=200°C. If VCE=4V, find the maximum collector current that the transistor can carry without destruction. What will be the allowed value of collector current if ambient temperature rises to 75°C?
Which of the following biasing techniques are prone to thermal runaway?
Thermal runaway in BJT will take place if the quiescent point is such that
Thermal runaway is not possible in FET because, as the temperature of FET increases