JEE Exam > JEE Tests > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Test: Types of Solids and Properties - JEE MCQ
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - JEE MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Types of Solids and Properties
Test: Types of Solids and Properties for JEE 2024 is part of Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced preparation. The Test: Types of Solids and Properties questions and answers have been
prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Types of Solids and Properties MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Types of Solids and Properties below.
Solutions of Test: Types of Solids and Properties questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE & Test: Types of Solids and Properties solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Types of Solids and Properties | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 1
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 2
Which of the following is not a crystalline solid?
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 3
Which one of the following forms a molecular solid when solidified?
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 4
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 5
What is the energy gap between valence band and conduction band in crystal of insulators?
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 5
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 6
In a solid 'AB' having the NaCl structure, 'A' atoms occupy the corners in cubic unit cell. If all the face-centered atoms along one of the axes are removed, then the resultant stoichiometry of the solid is
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 6
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 7
Assertion (A): White tin is an example of tetragonal system.
Reasoning (R): For a tetragonal system a = b = c and α = β = γ ≠ 90∘. The correct answer is
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 7
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 8
How many number of atoms are there in a cube based unit cell having one atom on each corner and two atoms on each body diagonal of cube?
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 8
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 9
The unit cell dimensions of a cubic lattice (edges a, b, c and the angles between them, α, β and γ) are
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 9
Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 10
A crystal made up of particles X, Y, and Z. X forms FCC& packing. Y occupies all octahedral voids of X and Z occupies all tetrahedral voids of X. If all particles along one body diagonal are removed, then the formula of the crystal is
Detailed Solution for Test: Types of Solids and Properties - Question 10
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Information about Test: Types of Solids and Properties Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Types of Solids and Properties solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Types of Solids and Properties, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Download as PDF


 form molecular solid.
form molecular solid.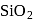 is a covalent network solid that forms a network of tetrahedral
is a covalent network solid that forms a network of tetrahedral  units.
units.  and
and 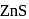 are ionic solids.
are ionic solids. atoms on the face-centres removing face-centred atoms along one of the
atoms on the face-centres removing face-centred atoms along one of the atoms.
atoms.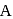 atoms per unit cell
atoms per unit cell
 atoms per unit cell
atoms per unit cell 


 & & & & Total number of atoms = 1 + 8 = 9.
& & & & Total number of atoms = 1 + 8 = 9.




















