Test: Western Political Thinkers - UGC NET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Western Political Thinkers
Match List I with List II
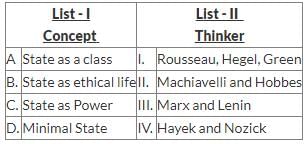
Choose the correct answer from the options given option

Who said, "Justice is the first virtue of social institutions".
Who was the disciple of Greek philosopher Socrates?
Who gave the concept of ‘Separation of Powers’ related to different forms of governments?
What is the nature of man, according to Aristotle?
Which of the following are correct?
A. Hannah Arendt - The Post-Modern Conditions
B. Jacques Derrida - The Post Card
C. Frantz Fanon - The Wretched of the Earth
D. Antonio Gramsci - The Human Condition
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The theory of social justice advanced by Rousseau and Hobbes, among others, is called -
According to Socrates which is not correct about the relationship between knowledge and virtue?



















