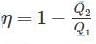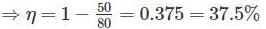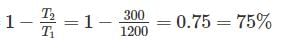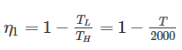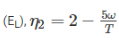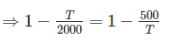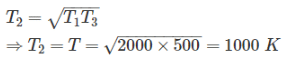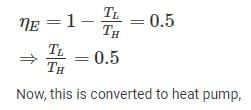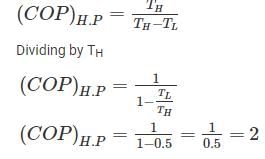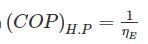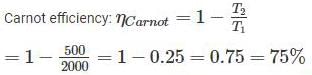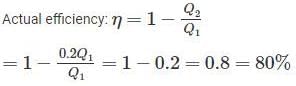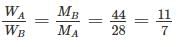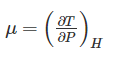Thermodynamics - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Thermodynamics - 1
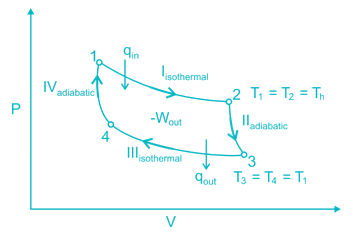
A thermodynamic cycle is composed of four processes. The heat added, and the work done in each process are as follows:
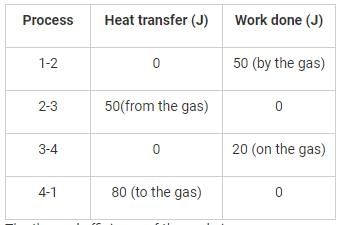
The thermal efficiency of the cycle is

A heat reservoir is maintained at 927 °C. If the ambient temperature is 27 °C, the availability of heat from the reservoir is limited to
Which of the following devices complies with the Clausius statement of the second law of thermodynamics?
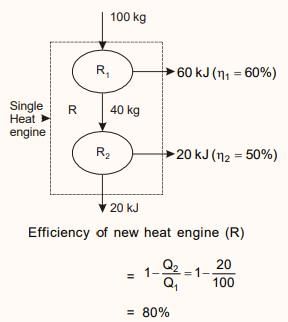
Two reversible engines are connected in series between a heat source and a sink. The efficiencies of these engines are 60% and 50%, respectively. If these two engines are replaced by a single reversible engine, the efficiency of this engine will be
The property of a working system which changes as the heat is supplied to the working fluid in a reversible manner is known as ________.
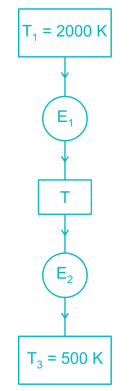
Two reversible heat engines operating between temperatures 2000 K and T K and T K and 500 K respectively. What is the intermediate temperature, if the efficiency of both the cycles is same?
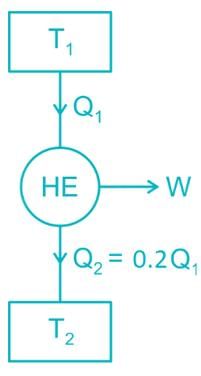
A Carnot heat engine is working with an efficiency of 50%. If the cycle is converted into a heat pump after reversing, then what is the coefficient of performance of the heat pump?
An inventor says, he has invented an engine which will reject 20% of heat absorbed from the source and the engine operates between 2000 K and 500 K. What kind of engine it is?
In a cyclic process, the work done by the system is 20 kJ, -30 kJ, -5 kJ and 10 kJ. What is the net heat (kJ) for the cyclic process?
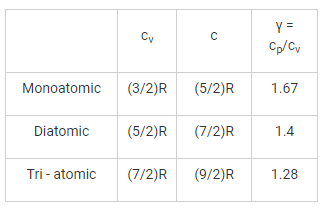
Which gas can attain the highest efficiency for the same compression rise?
A tank containing air is stirred by a paddle wheel. The work input to the paddle wheel is 9000 kJ and heat transferred to the surroundings from the tank is 3000 kJ. The external work done by the system is:
If pressure at any point in the liquid approaches the vapor pressure, liquid starts vaporising and creates pockets or bubbles of dissolved gases and vapours. This phenomenon is ________.
Two gases A and B with their molecular weights 28 and 44 respectively, expand at constant pressures through the same temperature range. The ratio of quantity of work done by the two gases (A : B) is ________.
A series of operations, which takes place in a certain order and restore the initial conditions at the end, is known as