Thermodynamics - 2 Test (17-12-2016) - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Thermodynamics - 2 Test (17-12-2016)
The entropy change involved in the isothermal reversible expansion of 2 moles of an ideal gas from a volume of 10 dm3 to a volume of 100 dm3 at 270C is:
For the process, 1 Ar (300 K, 1 bar), → 1 Ar (200 K, 10 bar) Assuming ideal gas behaviour the change in molar entropy is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The free energy change (ΔG) of 1 mole of an ideal gas that is compressed isothermally form 1 atm to 2 atm is:
In conversion of limestone to lime
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) the values of ΔH0 and ΔS0 are +179.1 kJ mol and 160.2 JK-1 respectively at 298 K and 1 bar. Assuming that ΔH0 and ΔS0 do not change with temperature, temperature above which conversion of limestone to lime will be spontaneous is:
Consider the following reactions:
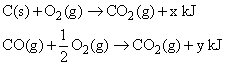
The heat of formation of CO(g) is:
In thermodynamic, a process is called reversible when:
Which of the following equations represents a reaction that provides the enthalpy of formation of CH3Cl2:
For 1 mole of a monoatomic ideal gas, the relation between pressure (P), volume (V) and average molecular kinetic energy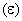 is:
is:
If enthalpy of hydrogenation of C6H6(l) into C6H12(l) is –205 kJ and resonance energy of C6H6(l) is –152 kJ/mol then enthalpy of hydrogenation of 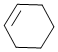 is assume ΔHVap of C6H6(l), C6H8(l), C6H12(l) all are equal:
is assume ΔHVap of C6H6(l), C6H8(l), C6H12(l) all are equal:
The standard free energies of formation of H2S(g) and CdS(s) at 1000°C are –49.0 kJ/mol and –127.2 kJ/mol respectively. Use these date to predict whether H2(g) will reduce CdS(s) to metallic Cd at this temperature:
if Δf H0 (C2H4) and Δf H0 (C2H6) are x1 and x2 kcal mol-1, then heat of hydrogenation of C2H4 is :
A monoatomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which the ratio of p to V at any instant is constant and equal to 1. What is the molar heat capacity of the gas:
The internal pressure of a Vander Wall’s gas is:
During the isothermal free expansion process the entropy of the surrounding & System respectively:
Consider the following data :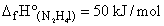
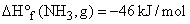 B.E (N-H) = 393 kJ/mol and B.E (H-H) = 436 Kj/mol
B.E (N-H) = 393 kJ/mol and B.E (H-H) = 436 Kj/mol 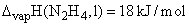 , The N–N bond energy in N2H4 is:
, The N–N bond energy in N2H4 is:
Among the following, intensive property is/are:
One mole of monoatomic ideal gas initially at a pressure of 2.0 bar and tamperture of 300 K is taken to a final pressure of 4.00 bar by a reversible path define by P/V = constant. Taking CV to be equal to 12.5 J mol-1K-1. The correct deduction for this process is/are:
Select the correct conditions indicated below the following plots:
The given graph represent the variations of Z Vs P, for the real gases A, B and C identify the only incorrect statement:
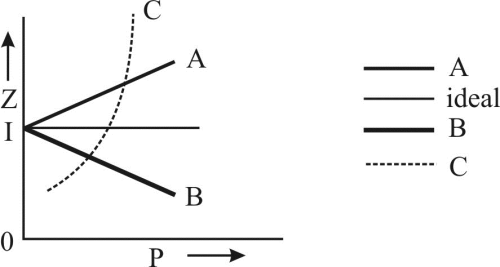
One mole of an ideal gas is subjected to a step reversible process (A - B and B - C ). The kpressure at A and C is same. Mark the correct statment(s):
A sample of gas is compressed at a pressure of 0.5 atmosphere form a volume of 40 mL to 200 mL. During the process 8.0 Joules of heat flows to the surrounding. Calculate the change in internal energy of the system
Given that standard molar enthalpies of formation of NO(g) and NO2(g) are respectively 90.3 kJ/mole and 33.2 kJ/mol, the enthalpy change for the reaction,
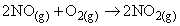 is (in kJ)
is (in kJ)
How many grams of oxygen are contained in 10.5 L of oxygen measured over water at 250C and 740 torr? Vapor pressure of water at 250C is 24 torr.
The coefficient of cubic expansion α and the isothermal compressibility β for metallic copper at 250C have value 49.2×10-6 K-1 and 7.747×10-6 MPa-1, respectively. Density of Cu at 250C is 8.93 g cm-3. Calculate Cp–Cv per mole for Cu.
0.35 mol of an ideal monoatomic gas is expanded adiabatically from a volume of 1 dm3 at 400 K to a volume of 5 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 50.65 KPa. What is the final temperature of the gas (in K)
A 2L vessel containing 2g of H2 gas at 27°C is connected to a 2L vessel containing 176 g of CO2 gas at 27°C. Assuming ideal behaviour of H2 and CO2, the particle pressure of H2 at equilibrium is ………………….bar:
2 mole of an ideal gas expanded isothermally and reversibly form 1L to 10L at 300 K. What is the enthalpy change:
50 ml of a gas A diffuse through a membrane in the same time as for the diffusion of 40 ml of gas B under identical condition of pressure and temperature. If the molecular mass of A is 64 that of B would be:
36 ml of pure water takes 100 sec to evaporate from a vessel and heater connected to an electric source.which delivers 806 watt.the ΔHvap of H2o is (in k j /mole)
0.5 mole each of two ideal gases A  and B
and B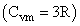 are taken in a container and expanded reversibly and adiabatically, during this process temp of gaseous mixture decreased from 350 K to 250 K find ΔH (in cal/mol) for the process:(in R gas constant)
are taken in a container and expanded reversibly and adiabatically, during this process temp of gaseous mixture decreased from 350 K to 250 K find ΔH (in cal/mol) for the process:(in R gas constant)

















