UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 10 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 10
Assertion (A): Environmental and social impact assessments never overlap with each other.
Reason (R): Environmental and social impact assessments are effectively opposite ends of the same spectrum.
Code:
Consider the following statements regarding ' Sacred Groves' :
1. They are fragments of forests of special religious importance protected by local communities.
2. They are a type of ex-situ conservation of biodiversity.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which one of the following in the correct sequence of economic integration between countries?
Assertion (A): Anti-cyclone leads to violent thunderstorms.
Reason (R): Anti-cyclones have high pressure at its centre.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
This ecosystem constitutes a systematic link between terrestrial and marine ecosystems
Which of the following factors influence the distribution of the population?
1. Landforms
2. Minerals
3. Soils
4. Industrialization
Select the correct answer from the code given below:
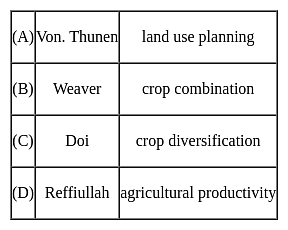
The following pairs are given about the contribution of geographer's in Agricultural geography and find out which is not correct?
The transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is crucial for addressing global warming because they:
Which of the following is NOT a direct consequence of global warming?
Which is not an effect of ocean current on the socio-economic and climatic condition of the coastal region?
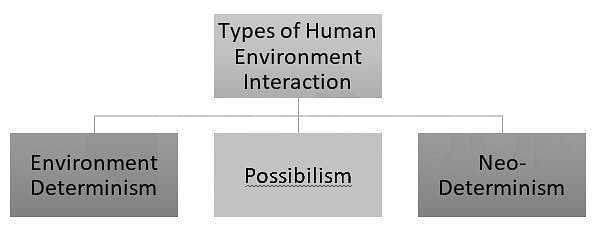
Which of the following are Model(s) of interaction between Human and Environment?
A tourist in Mumbai observes high tide near Gateway of India at 7.00 AM. At what time, he should expect another high tide on the same day?
Assertion (A)- Habitat shifts provide important evidence of population changes.
Reason (R) - Habitats are ecological space that are composed of multiple dimensions, each representing a biotic or abiotic ecological variable.
Heritage power project Sonapani mini-hydel power project is located in which state?
India's population growth is characterized by
|
16 docs|120 tests
|