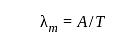UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 2 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 2
Who is the author of The Geographical Tradition (1993)?
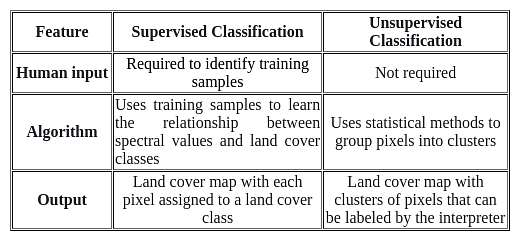
What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised classification in remote sensing image interpretation?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which is the lowest layer of the atmosphere?
Abiotic factors comprise of which of these?
(a) Raw materials are available at one fixed point.
(b) There is perfect competitive pricing
(c) The demand for the product is not constant.
(d) Transport rated may vary according to climatic and socio-economic conditions.
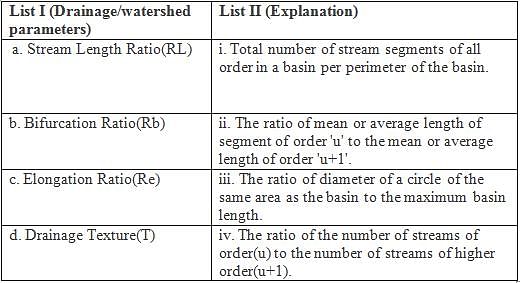
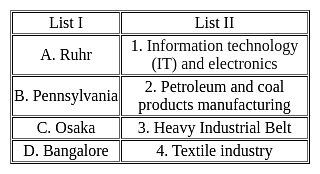
Match the List - I with List - II and select the correct answer from the code given below :

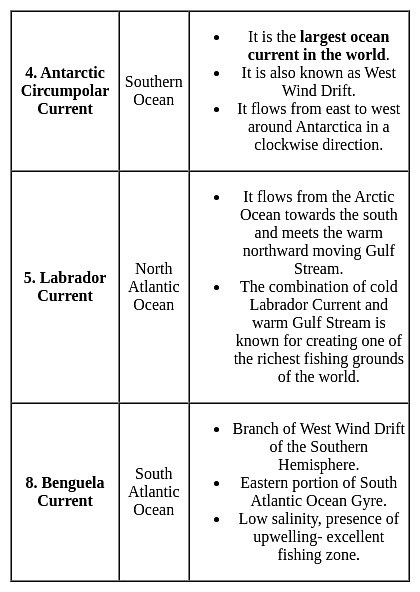
Which of the following is a warm ocean current?
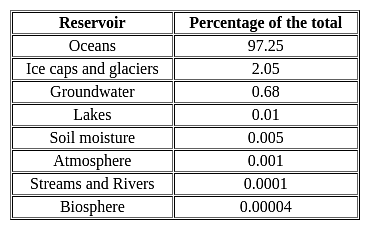
With reference to the water on the planet Earth, consider the following statements :
1. The amount of water in the rivers and lakes is more than the amount of groundwater.
2. The amount of water in polar ice caps and glaciers is more than the amount of groundwater.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
Match List – I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
As the temperature of the black body increases,the dominant wavelength of the emitted radiation according to Wein's displacement law is:
Consider the following statements about Equator and choose the correct option:
(A) The equator is a real line running on the globe, which divides it into two equal parts.
(B) The equator is the longest latitude.
(C) The equator represents the 180° latitude.
Consider the following statements about insolation and choose the correct option.
(A) Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth
(B) The amount and the intensity of the insolation vary during a day, in a second and in a year
(C) The amount of insolation increases from the equator towards the poles
Given below are two statements :
Assertion (A): According to the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1993, there were 16.5 million deaths due to infectious diseases worldwide.
Reason (R): Urbanisation without health planning leads to the spread of diseases.
Select from the codes given below:
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct answer using the code given below.
Assertion (A) : Central Business District (CBD) of a city has high concentration of wholesale stores, offices and cultural and recreational activities.
Reason (R) : Prices and demand of real increases as distance towards CBD reduces.
i. Goods have high demand with low prices.
ii. The demand curve rotated round the production point to give shape.
iii. As the competition increases, the market areas becomes hexagonal.
a) Weber's assumptions of a perfect competition with the spatial framework of a society has been criticized by many.
b) According to Losch, firms tend to locate at the most profitable of the production points.
c) E M Hoover used Isotims for joining places of equal transport costs.
d) D M Smith utilized the least cost approach of Weber with some of monopolistic -market area approach of Losch.
Which of the following options are correct?
(a) Monsoon break is the phenomenon which means monsoon rainfall stops for a couple of days.
(b) Western Ghats receive orographic rain during the monsoon.
(c) First rain in a place is called as monsoon burst.
(d) The El Nino current decreases the temperature of water.
Select the correct option:
Jarawas and Sentinelese tribes are found in which among the following state / Union Territory of India?
|
16 docs|120 tests
|