UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 4 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 4
Radcliffe Brown consider sociology as a science of__________.
_______refers the refurbishing or replacement of old buildings & new use of previously developed land in urban areas.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The peasant movements, revolts, riots, struggles, etc. in 19th century, India remained mainly localised because
Consider the following in relation to causes of urbanization and select the correct answer from the code given below:
1. High rate of emigration from rural to urban areas.
2. Increasing number of educational institutions in cities.
3. High rate of industrialization.
4. High standard of living in the rural area.
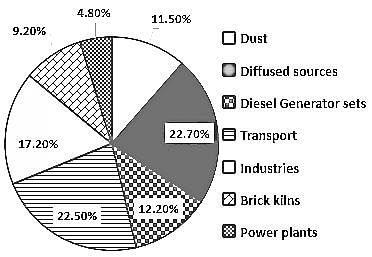
In mega cities of India, the dominant source of air pollution is
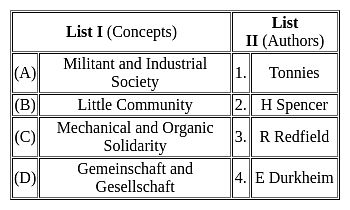
Match the List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below:

Given below are two statements
Statement I: Communication reflects the dimension of power.
Statement II: Power and unethical communication are strongly inter-related.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
According to Ethnomethodologists, which type of reasoning is used by the people?
Participatory research is also described as:
__________ constitutes the tangible things created by members of a society
Which of the following is the correct sequence of the evolution of marriage according to L.H. Morgan?
1. Synadyasmain
2. Monogamy
3. Group marriage
4. Consanguineous
5. Patriarchal
Choose the most appropriate sequence from the options given below:
Which of the following is the multi-purpose satellite system used in India for telecommunication and meteorological observation?
According to Dahrendrof the principal source of conflict in modern industrial societies is:
"A scientific theory of culture" is the work of:
Who has defined 'culture as a body of shared understandings'?
Who is known to have used the ‘Indological perspective’ in the study of Indian society?
(A) G. S. Ghurye
(B) Luis Dumont
(C) N. K. Bose
(D) M. N. Srinivas
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Who said, “ Economic Planning is a way of organizing and utilizing resources to maximum advantage in terms of defined social ends”?
Which of the following statement is correct?
- The strain theory states that society puts pressure on individuals to achieve socially accepted goals.
- When individuals feel strained, their course of action would fall between four modes of adaptation.
Which of the following statement is correct according to Agrarian Economy?
- An agrarian community is a community where everything is equally distributed.
- Traditional gender roles are prevalent in an agrarian economy.
|
16 docs|120 tests
|