UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 10 - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPPSC Mock Test Series 2025 - UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 10
Which of the following are not the objectives of Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act, 1996?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements regarding Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups.
- In 1973, the Balwant Rai Mehta Commission created Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs) as a separate category, who are less developed among the tribal groups.
- Among the 75 listed PVTG’s the highest number are found in Odisha (13), followed by Andhra Pradesh (12).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which railway station has been renamed as 'Veerangana Laxmibai Railway Station' by the Uttar Pradesh government?
In which one of the following States/UT, is the Lake Tsomgo located?
If the rupees per US Dollar exchange rate changes from Rs. 60 to Rs. 65 in a time period by the market forces, it implies:
Which of the following are the recommendations of the Sarkaria commission?
Consider the following personalities :
i. Annie Besant
ii. Lokmanya Tilak
iii. Jawahar Lal Nehru
iv. Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Who among the above participated in the Home Rule Movement ?
Rana Kumbha defeated __________ and erected the tower of victory (Vijay Stambha) in Chittorgarh.
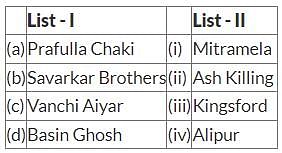
Match List - I with List - II and choose the correct answer from the codes given below :
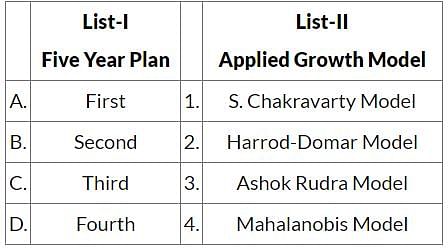
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following Articles mentioned under Part III of the Indian constitution:
1. Article 16
2. Article 29
3. Article 25
Which of the Articles given above are available only to citizens and not to foreigners?
Which type of gold coin is not issued by Skandagupta?
Arrange the following Pala rulers in chronological order.
(i) Devapala
(ii) Gopala
(iii) Mahipala
(iv) Dharmapala
Select the answer from the codes given below:
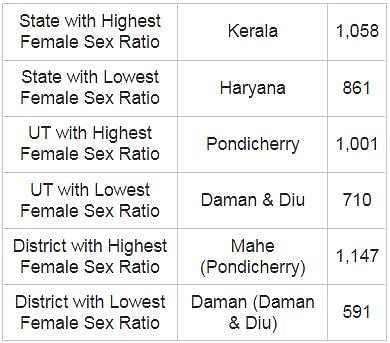
The sex ratio in rural areas of Uttar Pradesh as per the 2011 census was _______.
In the context of Indian Agriculture, what is the role of organic manures?
1. Organic manures bind the sandy soil and improve its water holding capacity.
2. They open the clayey soil and help in aeration better root growth.
3. They add plant nutrients in a small percentage and also add micro nutrients which are essential for plant growth.
Select the correct answer by using the codes given below.
Identify the correct statements from the following.
(A) Burning of wood is a physical and irreversible change.
(B) Boiling of water is a chemical and reversible change.
(C) Grinding wood into sawdust is a physical and irreversible change.
Consider the following about Pygmy hogs:
1. It is the smallest and rarest species of wild pig in the world.
2. Currently, the viable population of this pig in the wild is in the Kaziranga National Park & Tiger Reserve Assam.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Read the following statements:
(A) Dispute with respect to allocation of GST to a state is matter of dispute between two states.
(B) Dispute regarding sharing of river water is a matter of dispute between two states.
Select the correct answer:
In 1937, how many of the eleven provinces had Congress 'Prime Ministers' who functioned under the supervision of the British Governor?
The central component of Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan is-
What is the significance of the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) during elections?
What type of animal is a leopard classified as within the Big Cat family?
What is a common misconception about melanistic leopards?
How does the establishment of cyber police stations relate to the broader issue of cybercrime?
What is the Garud Commando Force known for in the Indian Air Force?
|
2 docs|37 tests
|