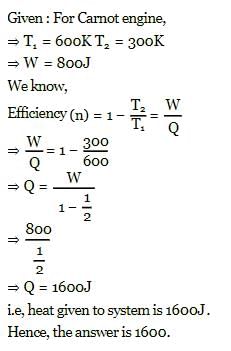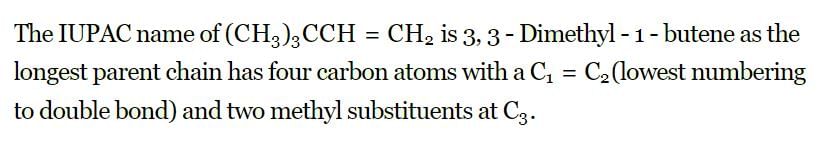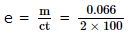VITEEE Chemistry Test - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test VITEEE: Subject Wise and Full Length MOCK Tests - VITEEE Chemistry Test - 2
To form propane-3-ethylpentan-3-ol, the reagents needed are
Aromatic aldehydes in the presence of cyanide ion as catalyst, are converted into acyloins. This reaction is called
When vapours of isopropyl alcohol are passed over heated copper, the major product obtained is
Which alkene gives the same product by the Markownikoff's and anti-Markownikoff's method
How many monochlorobutanes will be obtained on chlorination of n-butane?
The ratio of the molar amounts of H₂S needed to precipitate the metal ions from 20 mL each of 1M Cd(NO₃)₂ and 0.5 M CuSO₄ is
Which of the following acts as a source of energy in living systems?
Which of the following compounds on boiling with KMnO₄ and the subsequent acidification will not give benzoic acid ?
The heats of dissociation (k.cals/mole) of methane and ethane are 360 and 620 respectively. From these, C - C bond energy (k.cals/mole) in ethane can be evaluated as
A Carnot engine, working between 300 K to 600 K has a work output of 800 J-cycle⁻1. What is the amount of heat energy supplied to the engine from the source per cycle?
In which of the following neutralization reaction, the heat of neutralisation will be highest?
During the deepening of the colour of a dye, the absorption shifts towards red. This shifting is called
The IUPAC name of the compound having the formula (CH₃)₃C-CH =CH₂ is
[Co(NH₃)₄Cl₂]NO₂ and [Co(NH₃)₄ClNO₂]Cl exhibit which type of isomerism
Which of the following complexes is an outer orbital complex?
If a salt bridge is removed between the two half cells, the voltage
0.066 gram of metal was deposited when a current of 2 amperes is passed through a metal ion solution for 100 seconds. What is the electrochemical equivalent (in gram coulomb -1) of the metal?
A metal X on heating in nitrogen gas gives Y. Y on treatment with H₂O gives colourless gas which when passed through CuSO₄ solution gives blue colour. Y is
The ether that undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction is
The poisonous gas present in the exhaust fumes of cars is
|
1 videos|7 docs|63 tests
|
|
1 videos|7 docs|63 tests
|