Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Test: Matter in Our Surrounding - Class 9 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 9 - Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Test: Matter in Our Surrounding
What is the physical state of water at 100°C?
An Almirah is a solid because its
Find the incorrect statement
Which of the following does not affect rate of evaporation?
Convert 300K into Celsius
Arrange the following substances in increasing order of attraction between the particles: water, sugar, oxygen.
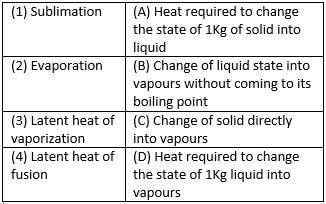
Match the following with correct response.
Name the state of matter that ‘has minimum interparticle attraction’
As the temperature of a solid increases, the particles gain more kinetic energy and start vibrating vigorously. Eventually, the forces of attraction between the particles are overcome and the solid changes into a liquid. The minimum temperature at which this happens (at atmospheric pressure) is called the:
Which of the following correctly describes the relative spaces between particles and their kinetic energy in the three states of matter?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the spaces and kinetic energy of particles in different states of matter?
The latent heat of vaporisation is the amount of heat energy required to:
Statement A: Celsius scale is the best scale for measuring temperature.
Statement B: CO2 (liquid state) is stored under high pressure.
Which of the two statements is true?
Find the incorrect statement
What is the physical state of water at 10°C?
|
84 videos|543 docs|60 tests
|



















