Test: The Tissue (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: The Tissue (Old NCERT)
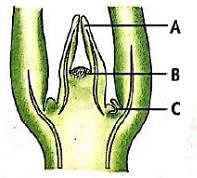
Select the option that correctly identifies the labellings A, B and C in the given figure showing section of root apical meristem.



Read the following statements regarding meristematic cells and select the correct ones.
(i) Cells possess the ability to grow and divide.
(ii) Cells have dense cytoplasm with prominent nucleus.
(iii) Well developed ER and mitochondria are present.
(i) Cells possess the ability to grow and divide.
(ii) Cells have dense cytoplasm with prominent nucleus.
(iii) Well developed ER and mitochondria are present.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
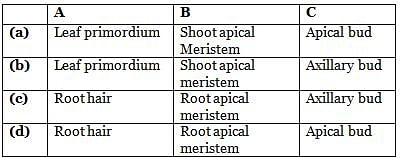
Idenitfy the given figure and select the correct option for A, B, C.


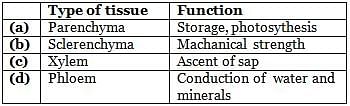
Which of the following tissues has dead cells with thick and lignified cell walls, having a few or numerous pits?
Both apical meristems and intercalary meristems are _______ meristems.
Identify the given figure and select the Correct option for the parts labelled as A, B and C.

Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Phloem parenchyma is absent in most monocots.
(ii) Gymnosperms lack tracheids and vessels.
(iii) Gymnosperms lack companion cells.
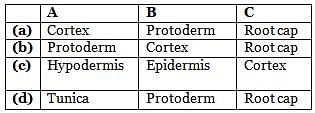
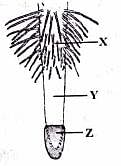
Identify the different zones of a typical root shown in figure and select the correct answer regarding these.
The growth of the roots and stems in length with the help of apical meristem is called
Increase in girth of the plant as a result of the activities of primary and secondary lateral maristems is called
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of meristematic cells?
A common structural feature of vessel elements and sieve tube elements is
All the xylem elements, when mature, are dead except
Which among the following is incorrect about tissues in a plant?
The cells of the quiescent centre are characterized by