Test: Lines & Angles- Case Based Type Questions - Class 9 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Class 9: Additional Practice - Test: Lines & Angles- Case Based Type Questions
Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.”

A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD.
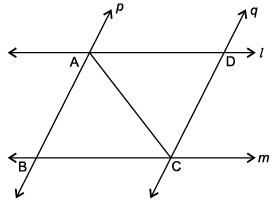
Q. If ∠BAC = 30°, find ∠ACD.


Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.”

A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD.
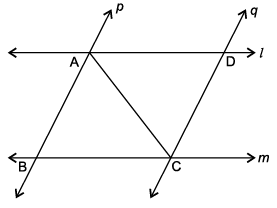
Q. ∠ABC + ∠BCD = 180° as :


Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.”

A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD.
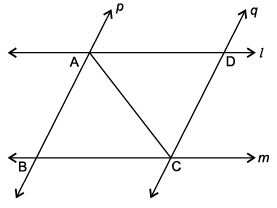
Q. If cow at C and cow at D is 2 km apart, then what is the distance between cow at A and cow at B?


Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.”

A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD.
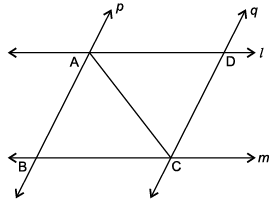
Q. If ∠B = 45°, then ∠D = _________ .
Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.”

A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD.
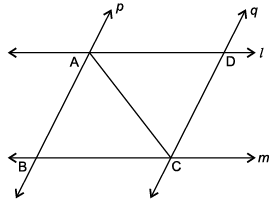
Q. If we join BD such that BD meet AC at O and ∠BOC = 30°, then what is the measure of ∠AOD?
Direction: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface.
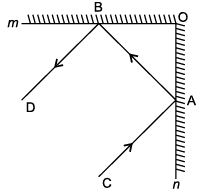
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. In figure, m and n are two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other.
Q. Parallel lines :
Direction: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface.
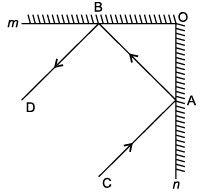
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. In figure, m and n are two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other.
Q. If BO = 3 cm, AB = 5 cm then, AO =
Direction: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface.
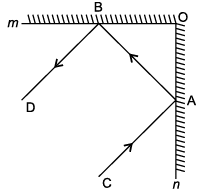
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. In figure, m and n are two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other.
Q. Which statement is incorrect ?
Direction: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface.
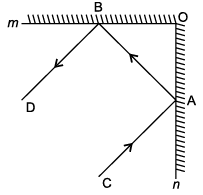
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. In figure, m and n are two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other.
Q. ∠DBA + ∠BAC
Direction: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface.
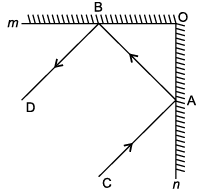
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. In figure, m and n are two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other.
Q. Incident ray CA is :
|
4 docs|108 tests
|


















