Test: Atoms and Molecules- Case Based Type Questions - Class 9 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Class 9: Additional Practice - Test: Atoms and Molecules- Case Based Type Questions
Direction: The following data represents the distribution of electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms of four elements A, B, C, D. Understand the data carefully and answer the following questions.
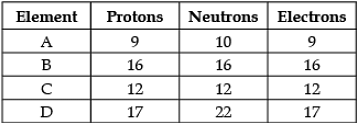
Q. Select the correct electronic distribution of element B:

Direction: The following data represents the distribution of electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms of four elements A, B, C, D. Understand the data carefully and answer the following questions.
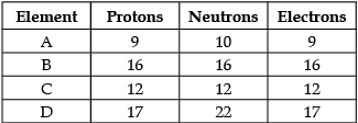
Q. The Mass number of element D is:

Direction: The following data represents the distribution of electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms of four elements A, B, C, D. Understand the data carefully and answer the following questions.
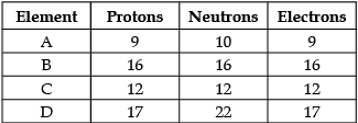
Q. The atomic number of element B is:

Direction: The following data represents the distribution of electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms of four elements A, B, C, D. Understand the data carefully and answer the following questions.
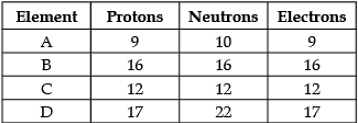
Q. The Valency of element A:
Direction: Sanjana observed that when 3.0 gm of carbon is burnt in 8.0 gm of oxygen, 11.0 gm of carbon dioxide is produced. Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
Q. Name the Law of Chemical Combination shown in the above passage:
Direction: Sanjana observed that when 3.0 gm of carbon is burnt in 8.0 gm of oxygen, 11.0 gm of carbon dioxide is produced. Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
Q. In what ratio does carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide?
Direction: Sanjana observed that when 3.0 gm of carbon is burnt in 8.0 gm of oxygen, 11.0 gm of carbon dioxide is produced. Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
Q. In a compound water at what ratio hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water:
Direction: Sanjana observed that when 3.0 gm of carbon is burnt in 8.0 gm of oxygen, 11.0 gm of carbon dioxide is produced. Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
Q. In a chemical substance, elements are present in a definite proportion by ______.
Direction: Two class students of class 9th, Aashi and Sheena, were asked to take 5.3 g of sodium carbonate and 6 g of ethanoic acid to make 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g of water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Aashi followed the instructions but Sheena took the chemicals without measuring their amounts.
Q. Which law does this agreements shows?
Direction: Two class students of class 9th, Aashi and Sheena, were asked to take 5.3 g of sodium carbonate and 6 g of ethanoic acid to make 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g of water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Aashi followed the instructions but Sheena took the chemicals without measuring their amounts.
Q. Whose activity do you think will be in agreement with the law?
Direction: Two class students of class 9th, Aashi and Sheena, were asked to take 5.3 g of sodium carbonate and 6 g of ethanoic acid to make 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g of water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Aashi followed the instructions but Sheena took the chemicals without measuring their amounts.
Q. The Law states that _______ can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Direction: Rahul took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container and Sohan also took 5 moles of sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
Q. Whose container has more number of atoms?
Direction: Rahul took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container and Sohan also took 5 moles of sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
Q. Which container is heavier?
Direction: Rahul took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container and Sohan also took 5 moles of sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
Q. Number of atoms in one mole:
Direction: Rahul took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container and Sohan also took 5 moles of sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
Q. The exact number of atoms present in 12 gm of Carbon-12:
|
4 docs|108 tests
|


















