Trueman Test: Anatomy of Flowering Plants (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Trueman Test: Anatomy of Flowering Plants (Old NCERT)
The tissue present in all organs of plant is:
Which among the following is correct about the anatomy of monocot root?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
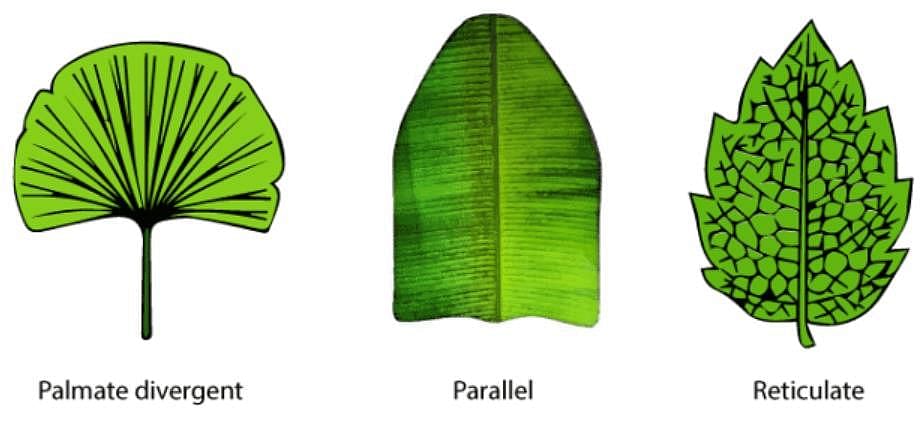
Reticulate venation is a characteristic in
Vascular bundles in which cambium is present between xylem and phloem is called as
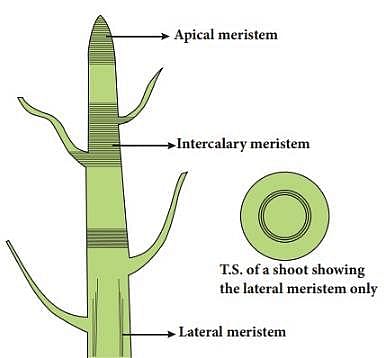
Which meristem contributes to the formation of the primary plant body?
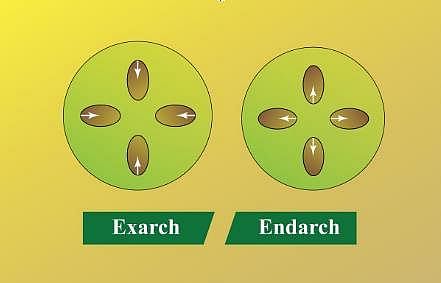
In angiosperms, vascular tissue develop from
Select the CORRECT statement.
In angiosperms, main water and mineral transporting elements are
Which epidermis of the leaf contains more stomata?
Bulliform or motor cells are present in
The parenchymatous cells which lie between the xylem and the phloem are called
Jute fibers deteriorate because they have
In arborescent monocots stem, a secondary cambium growing in the following type of vascular bundle is seen in
The layer just below the epidermis in a monocot stem is _________
Specialised parenchymatous cells, which are closely associated with sieve tube elements is
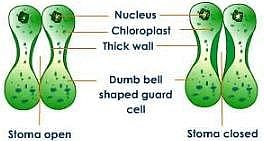
In monocotyledons, guard cell of stomata are
Which among the following is not correct about monocot stem?
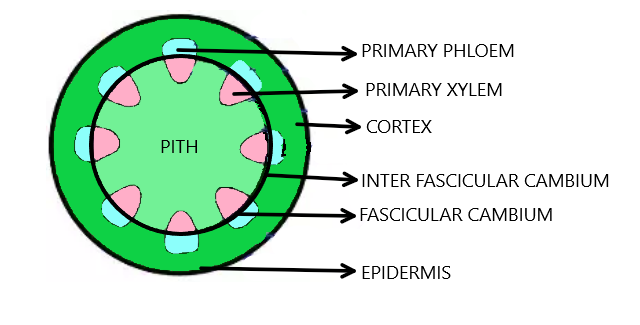
Which type of vascular bundle is shown in figure below
The meristems which occur at the tips of roots and shoots and produce primary tissues are called
Which one function is referred to as “Biological check post” ?
Stem of grasses and related plants elongate by the activity of
In dicot stems, the cells of cambium present between primary xylem and primary phloem is
A group of cells having a common origin and usually performing a common function is