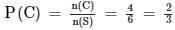Test: Probability Experimental Approach - Class 9 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Probability Experimental Approach
Empirical probability P (E) of an event happening is defined as:
If the probability of winning the game is 0.7 then, what is the probability of losing it?
One card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is either a red card or a king ?
An unbiased dice is thrown. What is the probability of getting an even number or a multiple of 3?
The maximum probability of an event of a trial is:
In an experiment, 100 drawing pins were dropped on a floor. 73 landed point up and the rest landed point down. A pin is selected at random and dropped. What is the probability that the pin will land point down?
What is the probability that a leap year has 53 Sundays?
In a simultaneous throw of a pair of dice, the probability of getting a sum more than 7 will be______.
Three unbiased coins are tossed. What is the probability of getting at most two heads?
An event for an experiment is defined as: