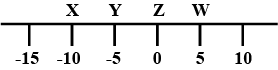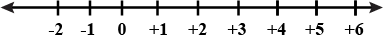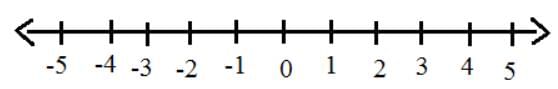Olympiad Test: Integers - Class 6 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics (Maths) Class 6 - Olympiad Test: Integers
By observing the above number line, state which of the following statements is true.
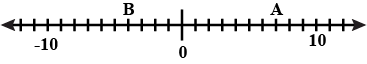
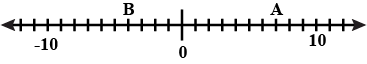
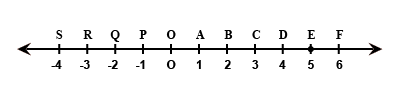
On the following number line value ‘zero’ is shown by the point
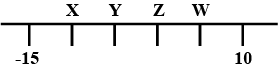
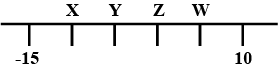
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
When the integers 10, 0, 5, 5, 7 are arranged in descending or ascending order, them find out which of the following integers always remains in the middle of the arrangement.
Answer the following using number line.
The integer which is 7 more than −4 is
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
Statement 1: When a positive integer and a negative integer are added, we always get a negative integer.
Statement 2: When two negative integers are added, we get a positive integer.
Which of the following option is not true with respect to given number line?
The integer 5 units to the right of 0 on the number line is:
The numbers on the left of 00 are ______ numbers and the numbers on the right of 00 are ________ numbers.
|
92 videos|348 docs|54 tests
|
|
92 videos|348 docs|54 tests
|