Test: Motion- Case Based Type Questions- 1 - Class 9 MCQ
5 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 9 - Test: Motion- Case Based Type Questions- 1
Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:
The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure.
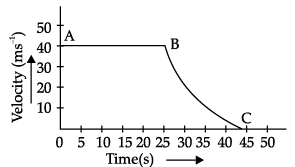
Q. Which of the following statement is correct?

Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:
The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure.
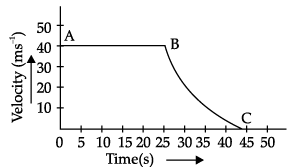
Q. Identify the part of graph where the object has zero acceleration. Give reasons for your answer.

Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:
The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure.

Q. State the kind of motion that objects has, from A to B and from B to C.

Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:
The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure.
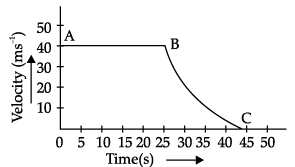
Q. Identify the part of graph where the object has negative acceleration. Give reasons for your answer.
Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:
The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure.
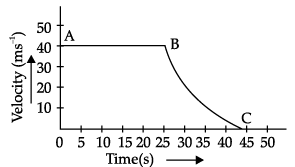
Q. The area enclosed by the velocity-time graph and the time axis represents the __________.
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|


















