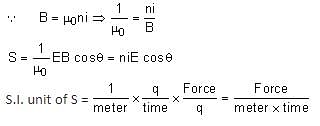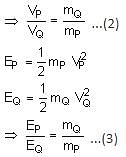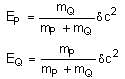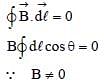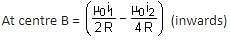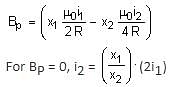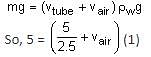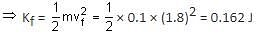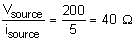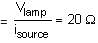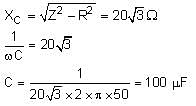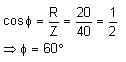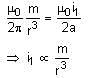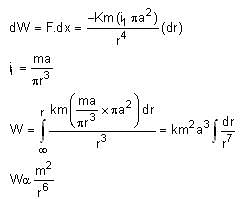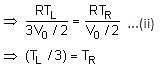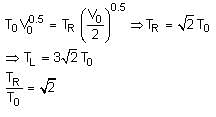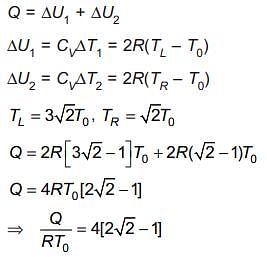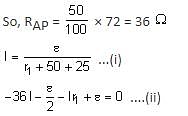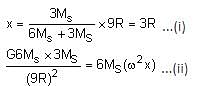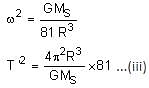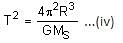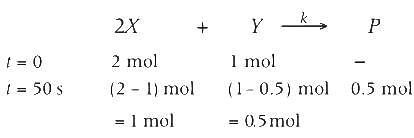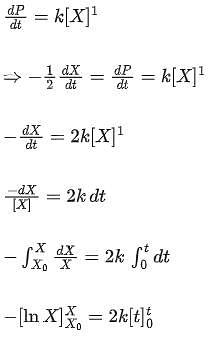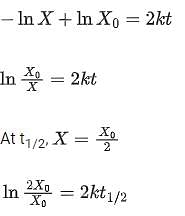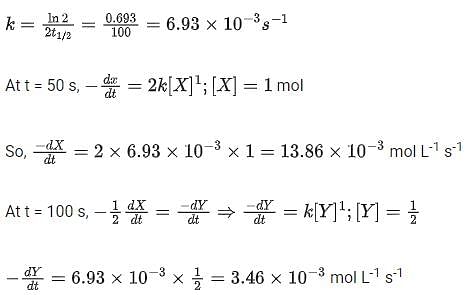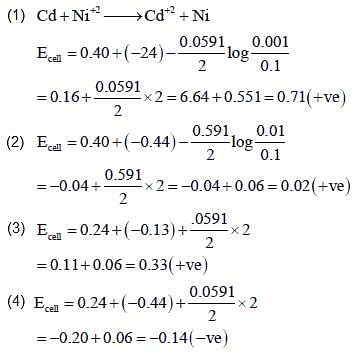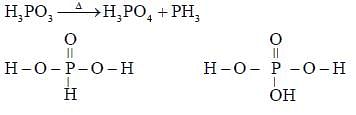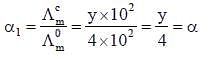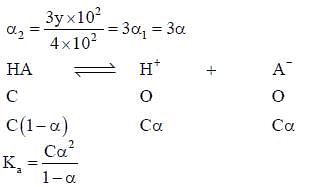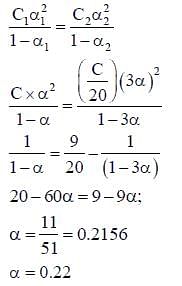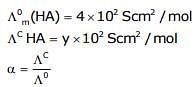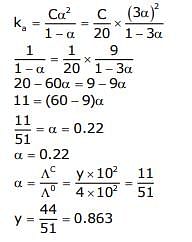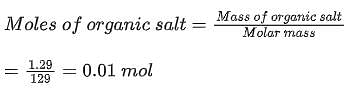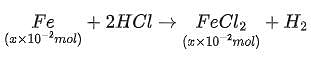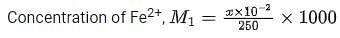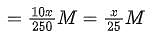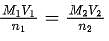JEE Advance 2021 Question Paper with Solutions - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advance 2021 Question Paper with Solutions - 2
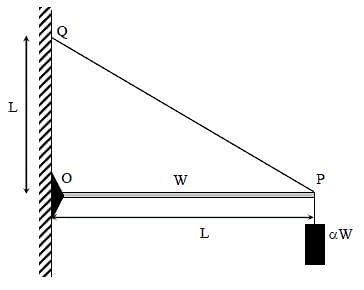
One end of a horizontal uniform beam of weight W and length L is hinged on a vertical wall at point O and its other end is supported by a light inextensible rope. The other end of the rope is fixed at point Q, at a height L above the hinge at point O. A block of weight α W is attached at the point P of the beam, as shown in the figure (not to scale). The rope can sustain a maximum tension of (2√2) W. Which of the following statements is/are correct?

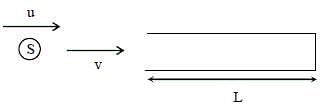
A source, approaching with speed u towards the open end of a stationary pipe of length L, is emitting a sound of frequency fs. The farther end of the pipe is closed. The speed of sound in air is v and f0 is the fundamental frequency of the pipe. For which of the following combinations of u and fS will the sound reaching the pipe lead to a resonance?
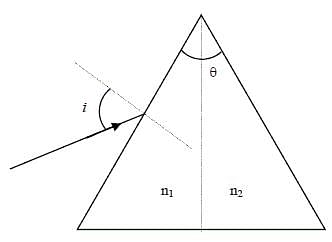
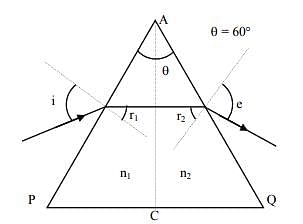
For a prism of prism angle θ = 60°, the refractive indices of the left half and the right half are, respectively, n1 and n2 (n2 ≥ n1) as shown in the figure. The angle of incidence i is chosen such that the incident light rays will have minimum deviation if n1 = n2 = n = 1.5. For the case of unequal refractive indices, n1 = n and n2 = n + Δn (where Δn << n), the angle of emergence e = i + Δe. Which of the following statements is/are correct?

A physical quantity 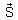 is defined as
is defined as 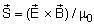 , where
, where 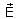 is electric field,
is electric field, 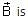 magnetic field and μ0 is the permeability of free space. The dimensions of
magnetic field and μ0 is the permeability of free space. The dimensions of 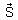 are the same as the dimensions of which of the following quantities?
are the same as the dimensions of which of the following quantities?
A heavy nucleus N, at rest, undergoes fission N → P + Q, where P and Q are two lighter nuclei. Let δ = MN - MP - MQ, where MP, MQ and MN are the masses of P, Q and N, respectively. EP and EQ are the kinetic energies of P and Q, respectively. The speeds of P and Q are VP and VQ, respectively. If c is the speed of light, which of the following statements is/are correct?
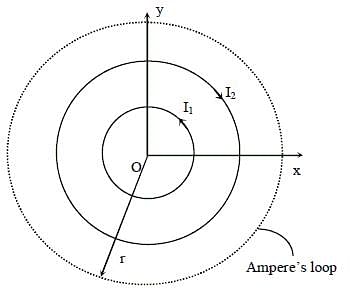
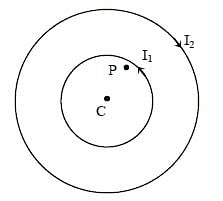
Two concentric circular loops, one of radius R and the other of radius 2R, lie in the xy-plane with the origin as their common centre, as shown in the figure. The smaller loop carries current I1 in the anti-clockwise direction and the larger loop carries current I2 in the clockwise direction, with I2 > 2I1. 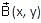 denotes the magnetic field at a point (x, y) in the xy-plane. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
denotes the magnetic field at a point (x, y) in the xy-plane. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
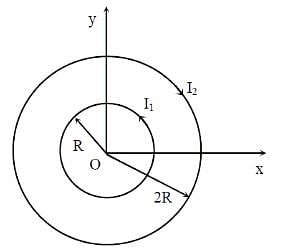
A soft plastic bottle, filled with water of density 1 gm/cc, carries an inverted glass test tube with some air (ideal gas) trapped as shown in the figure. The test tube has a mass of 5 gm, and it is made of a thick glass of density 2.5 gm/cc.
Initially the bottle is sealed at atmospheric pressure p0 = 105 Pa so that the volume of the trapped air is v0 = 3.3 cc. When the bottle is squeezed from outside at constant temperature, the pressure inside rises and the volume of the trapped air reduces. It is found that the test tube begins to sink at pressure p0 + Δp without changing its orientation.
At this pressure, the volume of the trapped air is v0 - Δv.
Let Δv = X cc and Δp = Y x 103 Pa.
Q. The value of X is _______.
A soft plastic bottle, filled with water of density 1 gm/cc, carries an inverted glass test tube with some air (ideal gas) trapped as shown in the figure. The test tube has a mass of 5 gm, and it is made of a thick glass of density 2.5 gm/cc.
Initially the bottle is sealed at atmospheric pressure p0 = 105 Pa so that the volume of the trapped air is v0 = 3.3 cc. When the bottle is squeezed from outside at constant temperature, the pressure inside rises and the volume of the trapped air reduces. It is found that the test tube begins to sink at pressure p0 + Δp without changing its orientation.
At this pressure, the volume of the trapped air is v0 - Δv.
Let Δv = X cc and Δp = Y x 103 Pa.
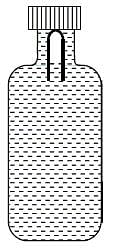
Q. The value of Y is _______.
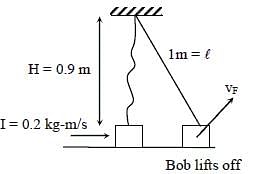
A pendulum consists of a bob of mass m = 0.1 kg and a massless inextensible string of length L = 1.0 m. It is suspended from a fixed point at height H = 0.9 m above a frictionless horizontal floor. Initially, the bob of the pendulum is lying on the floor at rest vertically below the point of suspension. A horizontal impulse P = 0.2 kg-m/s is imparted to the bob at some instant. After the bob slides for some distance, the string becomes taut and the bob lifts off the floor. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the pendulum about the point of suspension just before the bob lifts off is J kg-m2/s. The kinetic energy of the pendulum just after the lift-off is K joules.
Q. The value of J is ______.
A pendulum consists of a bob of mass m = 0.1 kg and a massless inextensible string of length L = 1.0 m. It is suspended from a fixed point at height H = 0.9 m above a frictionless horizontal floor. Initially, the bob of the pendulum is lying on the floor at rest vertically below the point of suspension. A horizontal impulse P = 0.2 kg-m/s is imparted to the bob at some instant. After the bob slides for some distance, the string becomes taut and the bob lifts off the floor. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the pendulum about the point of suspension just before the bob lifts off is J kg-m2/s. The kinetic energy of the pendulum just after the lift-off is K joules.
Q. The value of K is ______.
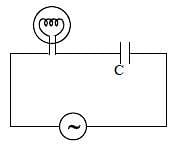
In the circuit, a metal filament lamp is connected in series with a capacitor of capacitance CμF across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply. The power consumed by the lamp is 500 W while the voltage drop across it is 100 V. Assume that there is no inductive load in the circuit. Take rms values of the voltages. The magnitude of the phase angle (in degrees) between the current and supply voltage is ϕ. Assume π√3 ≈ 5.
Q. The value of C is _____.
In the circuit, a metal filament lamp is connected in series with a capacitor of capacitance CμF across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply. The power consumed by the lamp is 500 W while the voltage drop across it is 100 V. Assume that there is no inductive load in the circuit. Take rms values of the voltages. The magnitude of the phase angle (in degrees) between the current and supply voltage is ϕ. Assume π√3 ≈ 5.
Q. The value of ϕ is _____.
A special metal S conducts electricity without any resistance. A closed wire loop, made of S, does not allow any change in flux through itself by inducing a suitable current to generate a compensating flux.
The induced current in the loop cannot decay due to its zero resistance. This current gives rise to a magnetic moment which in turn repels the source of magnetic field or flux. Consider such a loop, of radius a, with its centre at the origin. A magnetic dipole of moment m is brought along the axis of this loop from infinity to a point at distance r (>> a) from the centre of the loop with its north pole always facing the loop, as shown in the figure below.
The magnitude of magnetic field of a dipole m, at a point on its axis at distance r, is  , where μ0 is the permeability of free space. The magnitude of the force between two magnetic dipoles with moments, m1 and m2, separated by a distance r on the common axis, with their north poles facing each other, is
, where μ0 is the permeability of free space. The magnitude of the force between two magnetic dipoles with moments, m1 and m2, separated by a distance r on the common axis, with their north poles facing each other, is 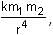 , where k is a constant of appropriate dimensions. The direction of this force is along the line joining the two dipoles.
, where k is a constant of appropriate dimensions. The direction of this force is along the line joining the two dipoles.
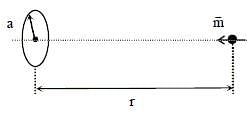
Q. When the dipole m is placed at a distance r from the centre of the loop (as shown in the figure), the current induced in the loop will be proportional to
A special metal S conducts electricity without any resistance. A closed wire loop, made of S, does not allow any change in flux through itself by inducing a suitable current to generate a compensating flux.
The induced current in the loop cannot decay due to its zero resistance. This current gives rise to a magnetic moment which in turn repels the source of magnetic field or flux. Consider such a loop, of radius a, with its centre at the origin. A magnetic dipole of moment m is brought along the axis of this loop from infinity to a point at distance r (>> a) from the centre of the loop with its north pole always facing the loop, as shown in the figure below.
The magnitude of magnetic field of a dipole m, at a point on its axis at distance r, is 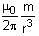 , where μ0 is the permeability of free space. The magnitude of the force between two magnetic dipoles with moments, m1 and m2, separated by a distance r on the common axis, with their north poles facing each other, is
, where μ0 is the permeability of free space. The magnitude of the force between two magnetic dipoles with moments, m1 and m2, separated by a distance r on the common axis, with their north poles facing each other, is 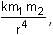 , where k is a constant of appropriate dimensions. The direction of this force is along the line joining the two dipoles.
, where k is a constant of appropriate dimensions. The direction of this force is along the line joining the two dipoles.
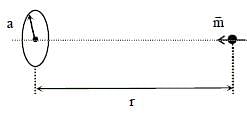
Q. The work done in bringing the dipole from infinity to a distance r from the centre of the loop by the given process is proportional to
A thermally insulating cylinder has a thermally insulating and frictionless movable partition in the middle, as shown in the figure below. On each side of the partition, there is one mole of an ideal gas, with specific heat at constant volume, CV = 2R. Here, R is the gas constant. Initially, each side has a volume V0 and temperature T0. The left side has an electric heater, which is turned on at very low power to transfer heat Q to the gas on the left side. As a result the partition moves slowly towards the right reducing the right side volume to V0/2. Consequently, the gas temperatures on the left and the right sides become TL and TR, respectively. Ignore the changes in the temperatures of the cylinder, heater and the partition.
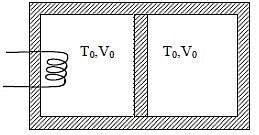
Q. The value of TR/T0 is
A thermally insulating cylinder has a thermally insulating and frictionless movable partition in the middle, as shown in the figure below. On each side of the partition, there is one mole of an ideal gas, with specific heat at constant volume, CV = 2R. Here, R is the gas constant. Initially, each side has a volume V0 and temperature T0. The left side has an electric heater, which is turned on at very low power to transfer heat Q to the gas on the left side. As a result the partition moves slowly towards the right reducing the right side volume to V0/2. Consequently, the gas temperatures on the left and the right sides become TL and TR, respectively. Ignore the changes in the temperatures of the cylinder, heater and the partition.

Q. The value of Q/RT0 is
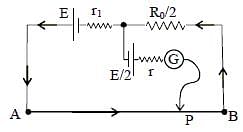
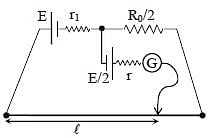
In order to measure the internal resistance r1 of a cell of emf E, a meter bridge of wire resistance R0 = 50Ω , a resistance R0/2, another cell of emf E/2 (internal resistance r) and a galvanometer G are used in a circuit, as shown in the figure. If the null point is found at ℓ = 72 cm, then the value of r1 = ___Ω.
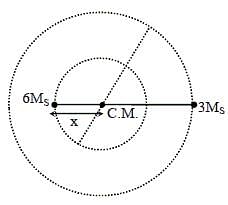
The distance between two stars of masses 3MS and 6MS is 9R. Here, R is the mean distance between the centres of the Earth and the Sun, and MS is the mass of the Sun. The two stars orbit around their common centre of mass in circular orbits with period nT, where T is the period of Earth's revolution around the Sun.
Q. The value of n is ______.
In a photoemission experiment, the maximum kinetic energies of photoelectrons from metals P, Q and R are EP, EQ and ER, respectively, and they are related by EP = 2EQ = 2ER. In this experiment, the same source of monochromatic light is used for metals P and Q while a different source of monochromatic light is used for the metal R. The work functions for metals P, Q and R are 4.0 eV, 4.5 eV and 5.5 eV, respectively. The energy of the incident photon used for metal R, in eV, is ______.
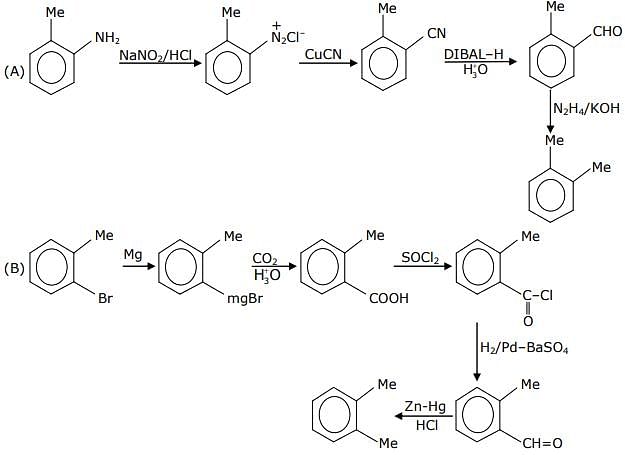
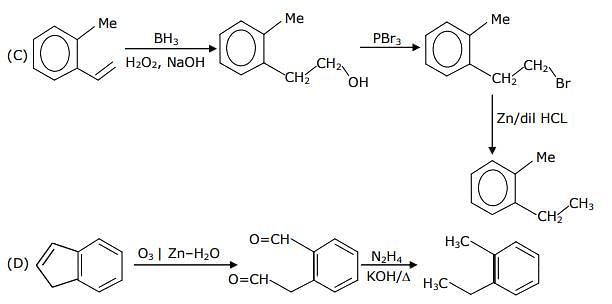
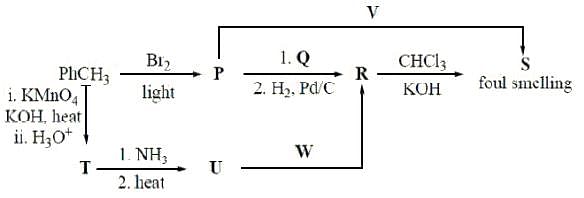
The reaction sequence(s) that would lead to o-xylene as the major product is/are
Correct option(s) for the following sequence of reactions is/are:
For the following reaction 2X + Y 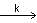 P, the rate of reaction is d[P]/dt = k[X]. Two moles of X are mixed with one mole of Y to make 1.0 L of solution. At 50 s, 0.5 mole of Y is left in the reaction mixture. The correct statement(s) about the reaction is/are:
P, the rate of reaction is d[P]/dt = k[X]. Two moles of X are mixed with one mole of Y to make 1.0 L of solution. At 50 s, 0.5 mole of Y is left in the reaction mixture. The correct statement(s) about the reaction is/are:
(Use ln 2 = 0.693)
Some standard electrode potentials at 298 K are given below:
Pb2+/Pb - 0.13 V
Ni2+/Ni - 0.24 V
Cd2+/Cd - 0.40 V
Fe2+/Fe - 0.44 V
To a solution containing 0.001 M of X2+ and 0.1 M of Y2+, the metal rods X and Y are inserted (at 298 K) and connected by a conducting wire. This resulted in dissolution of X. The correct combination(s) of X and Y, respectively, is/are:
(Given: Gas constant, R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, Faraday constant, F = 96,500 C mol-1)
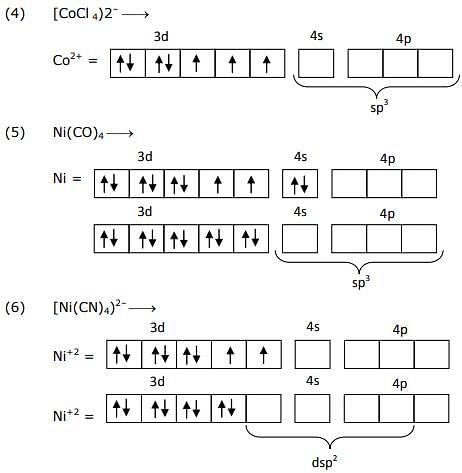
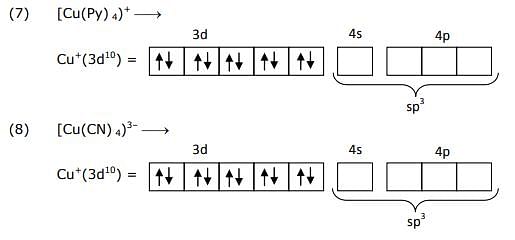
The pair(s) of complexes wherein both exhibit tetrahedral geometry is/are
(Note: py = pyridine; Given: Atomic numbers of Fe, Co, Ni and Cu are 26, 27, 28 and 29, respectively)
The correct statement(s) related to oxoacids of phosphorus is/are:
At 298 K, the limiting molar conductivity of a weak monobasic acid is 4 x 102 S cm2 mol-1. At 298 K, for an aqueous solution of the acid, the degree of dissociation is and the molar conductivity is y x 102 S cm2 mol-1. At 298 K, upon 20 times dilution with water, the molar conductivity of the solution becomes 3y x 102 S cm2 mol-1.
Q. The value of α is _______.
At 298 K, the limiting molar conductivity of a weak monobasic acid is 4 x 102 S cm2 mol-1. At 298 K, for an aqueous solution of the acid, the degree of dissociation is and the molar conductivity is y x 102 S cm2 mol-1. At 298 K, upon 20 times dilution with water, the molar conductivity of the solution becomes 3y x 102 S cm2 mol-1.
Q. The value of y is _______.
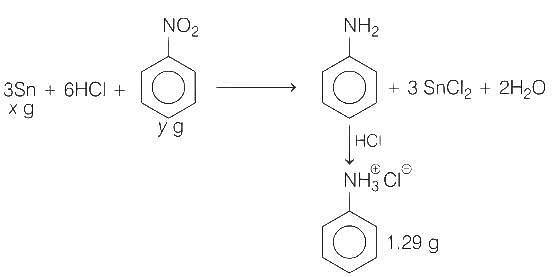
Reaction of x g of Sn with HCl quantitatively produced a salt. Entire amount of the salt reacted with y g of nitrobenzene in the presence of required amount of HCl to produce 1.29 g of an organic salt (quantitatively).
(Use Molar masses (in g mol-1) of H, C, N, O, Cl and Sn as 1, 12, 14, 16, 35 and 119, respectively)
Q. The value of x is _______.
Reaction of x g of Sn with HCl quantitatively produced a salt. Entire amount of the salt reacted with y g of nitrobenzene in the presence of required amount of HCl to produce 1.29 g of an organic salt (quantitatively).
(Use Molar masses (in g mol-1) of H, C, N, O, Cl and Sn as 1, 12, 14, 16, 35 and 119, respectively)
Q. The value of y is _______.
A sample (5.6 g) containing iron is completely dissolved in cold dilute HCl to prepare a 250 mL of solution. Titration of 25.0 mL of this solution requires 12.5 mL of 0.03 M KMnO4 solution to reach the end point. Number of moles of Fe2+ present in 250 mL solution is x × 10−2 (consider complete dissolution of FeCl2). The amount of iron present in the sample is y% by weight.
(Assume: KMnO4 reacts only with Fe2+ in the solution, Use: Molar mass of iron as 56 g mol−1)
Q. The value of x is _______.


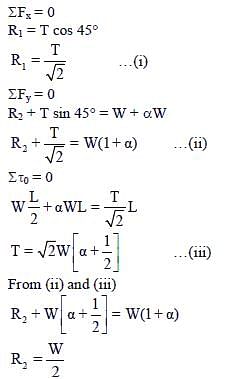
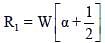
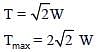
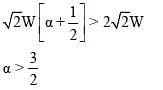
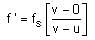
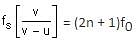
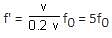
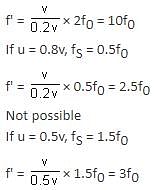


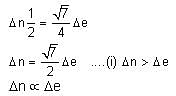

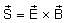
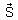 is the pointing vector which is defined as energy flowing per unit area in unit time.
is the pointing vector which is defined as energy flowing per unit area in unit time.