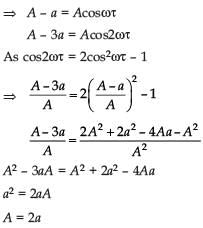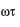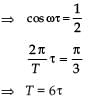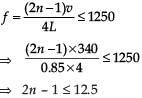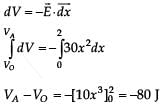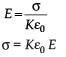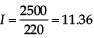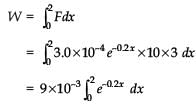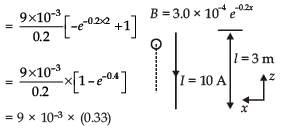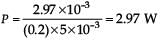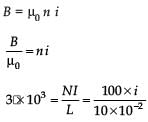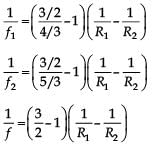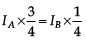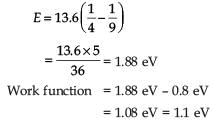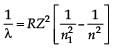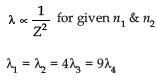JEE Main 2014 April 6 Paper & Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main 2014 April 6 Paper & Solutions
The current voltage relation of diode is given by I = (e1000V/T – 1) mA, where the applied V is in volts and the temperature T is in degree kelvin. If a student makes an error measuring ± 0.01 V while measuring the current of 5 mA at 300 K, what will be the error in the value of current in mA?
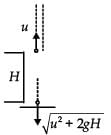
From a tower of height H, a particle is thrown vertically upwards with a speed u. The time taken by the particle, to hit the ground, is n times that taken by it to reach the highest point of its path. The relation between H, u and n is:
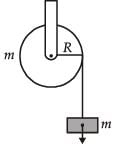
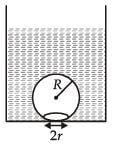
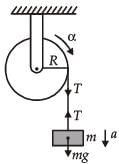
A mass m is supported by a massless string wound around a uniform hollow cylinder of mass m and radius R. If the string does not slip on the cylinder, with what acceleration will the mass fall on release?

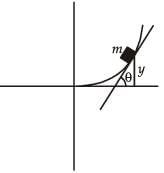
A block of mass m is placed on a surface with a vertical cross-section given by y = x3/6. f the coefficient of friction is 0.5, the maximum height above the ground at which the block can be placed without slipping is
When a rubber-band is stretched by a distance x, it exerts a restoring force of magnitude F = ax + bx2 where a and b are constants. The work done in stretching the unstretched rubber-band by L is :
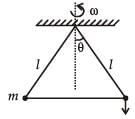
A bob of mass m attached to an inextensible string of length l is suspended from a vertical support.
The bob rotates in a horizontal circle with an angular speed ω rad/s about the vertical. About the point of suspension
Four particles, each of mass M and equidistant from each other, move along a circle of radius R under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each particle is
The pressure that has to be applied to the ends of a steel wire of length 10 cm to keep its length constant when its temperature is raised by 100°C is :
(For steel Young's modulus is 2 × 1011 Nm–2 and coefficient of thermal expansion is 1.1 × 10–5 K–1)
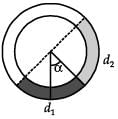
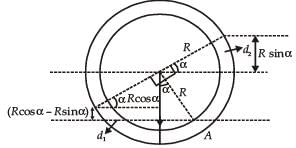
There is a circular tube in a vertical plane. Two liquids which do not mix and of densities d1 and d2 are filled in the tube. Each liquid subtends 90° angle at centre. Radius joining their interface makes an angle α with vertical. Ratio 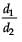 is
is
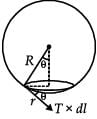
On heating water, bubbles being formed at the bottom of the vessel detatch and rise. Take the bubbles to be spheres of radius R and making a circular contact of radius r with the bottom of the vessel. If r << R, and the surface tension of water is T, value of r just before bubbles detatch is (Density of water is ρω)
Three rods of copper, brass and steel are welded together to form a Y-shaped structure. Area of cross-section of each rod = 4 cm2. End of copper rod is maintained at 100°C whereas ends of brass and steel are kept at 0°C. Lengths of the copper, brass and steel rods are 46, 13 and 12 cm respectively. The rods are thermally insulated from surroundings except at ends. Thermal conductivities of copper, brass and steel are 0.92, 0.26 and 0.12 CGS units respectively. Rate of heat flow through copper rod is
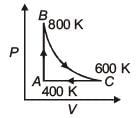
One mole of diatomic ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process ABC as shown in figure. The process BC is adiabatic. The temperatures at A, B and C are 400 K, 800 K and 600 K respectively. Choose the correct statement
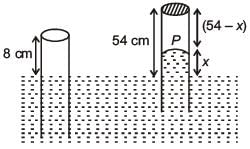
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of 8 cm extends above the mercury level. The open end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by additional 46 cm. What will be length of the air column above mercury in the tube now?
(Atmospheric pressure = 76 cm of Hg)
A particle moves with simple harmonic motion in a straight line. In first τ s, after starting from rest it travels a distance a, and in next τ s, it travels 2a in same direction then
A pipe of length 85 cm is closed from one end. Find the number of possible natural oscillations of air column in the pipe whose frequencies lie below 1250 Hz. The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s.
Assume that an electric field 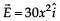 exists in space. Then the potential difference VA – VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is
exists in space. Then the potential difference VA – VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is
A parallel plate capacitor is made of two circular plates separated by a distance 5 mm and with a dielectric of dielectric constant 2.2 between them. When the electric field in the dielectric is 3 × 104 V/m, the charge density of the positive plate will be close to
In a large building, there are 15 bulbs of 40 W, 5 bulbs of 100 W, 5 fans of 80 W and 1 heater of 1 kW. The voltage of the electric mains is 220 V. The minimum capacity of the main fuse of the building will be:
A conductor lies along the z-axis at –1.5 ≤ z < 1.5 m and carries a fixed current of 10.0 A in direction (see figure). For a field
direction (see figure). For a field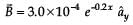 T, find the power required to move the conductor at constant speed to x = 2.0 m, y = 0 m in 5 × 10–3 s. Assume parallel motion along the x-axis
T, find the power required to move the conductor at constant speed to x = 2.0 m, y = 0 m in 5 × 10–3 s. Assume parallel motion along the x-axis
The coercivity of a small magnet where the ferromagnet gets demagnetized is 3 × 103 A m–1. The current required to be passed in a solenoid of length 10 cm and number of turns 100, so that the magnet gets demagnetized when inside the solenoid, is
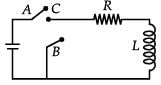
In the circuit shown here, the point 'C' is kept connected to point 'A' till the current flowing through the circuit becomes constant. Afterward, suddenly, point 'C' is disconnected from point 'A' and connected to point 'B' at time t = 0. Ratio of the voltage across resistance and the inductor at t = L/R will be equal to
During the propagation of electromagnetic waves in a medium
A thin convex lens made from crown glass 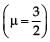 has focal length f. When it is measured in two different liquids having refractive indices 4/3 and 5/3, it has the focal lengths f1 and f2 respectively. The correct relation between the focal lengths is
has focal length f. When it is measured in two different liquids having refractive indices 4/3 and 5/3, it has the focal lengths f1 and f2 respectively. The correct relation between the focal lengths is
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle(θ). Select the correct statement
Two beams, A and B, of plane polarized light with mutually perpendicular planes of polarization are seen through a polaroid. From the position when the beam A has maximum intensity (and beam B has zero intensity), a rotation of polaroid through 30° makes the two beams appear equally bright. If the initial intensities of the two beams are IA and IB respectively, then 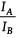 equals
equals
The radiation corresponding to 3→2 transitions of hydrogen atoms falls on a metal surface to produce photoelectrons. These electrons are made to enter a magnetic field of 3 × 10–4 T. If the radius of the largest circular path followed by these electrons is 10.0 mm, the work function of the metal is close to
Hydrogen (1H1), Deuterium (1H2), singly ionised Helium (2He4)+ and doubly ionised lithium (3Li6)++ all have one electron around the nucleus. Consider an electron transition from n = 2 to n = 1. If the wavelengths of emitted radiation are λ1, λ2, λ3 and λ4 respectively then approximately which one of the following is correct?
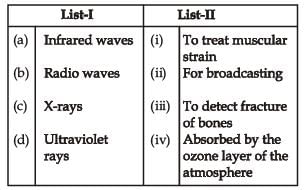
Match List-I (Electromagnetic wave type) with List-II (Its association/application) and select the correct option from the choices given below the lists :

A student measured the length of a rod and wrote it as 3.50 cm. Which instrument did he use to measure it?


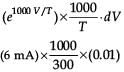
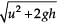
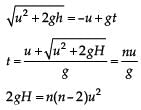

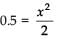
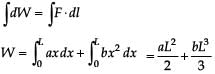
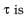 perpendicular to
perpendicular to 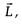 direction of L changes but magnitude remains same.
direction of L changes but magnitude remains same.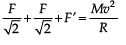
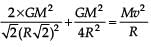
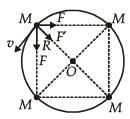
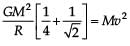
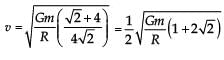
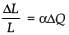
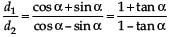
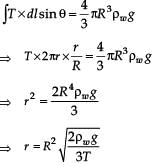
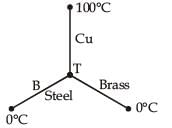
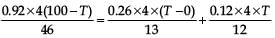
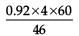 = 4.8 cal/s
= 4.8 cal/s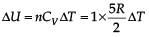
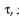 , x = A – a
, x = A – a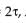 , x = A – 3a
, x = A – 3a