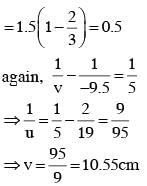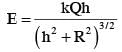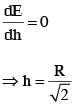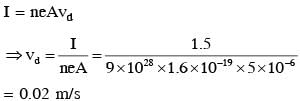JEE Main 2019 January 9 Shift 1 Paper & Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main 2019 January 9 Shift 1 Paper & Solutions
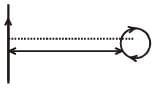
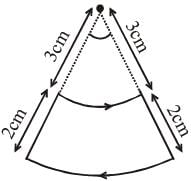
A current loop, having two circular arcs joined by two radial lines is shown in the figure. It carries a current of 10 A. The magnetic field at point O will be close to :


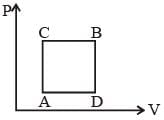
A gas can be taken from A to B via two different processes ACB and ADB.
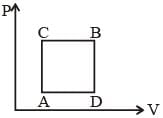
When path ACB is used 60 J of heat flows into the system and 30 J of work is done by the system. If path ADB is used work done by the system is 10 J. The heat Flow into the system in path ADB is :

When path ACB is used 60 J of heat flows into the system and 30 J of work is done by the system. If path ADB is used work done by the system is 10 J. The heat Flow into the system in path ADB is :
A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency 50 MHz travels in free space along the positive xdirection. At a particular point in space and time, 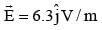 The corresponding magnetic field
The corresponding magnetic field 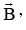 at that point will be:
at that point will be:
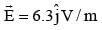 The corresponding magnetic field
The corresponding magnetic field 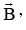 at that point will be:
at that point will be:Two coherent sources produce waves of different intensities which interfere. After interference, the ratio of the maximum intensity to the minimum intensity is 16. The intensity of the waves are in the ratio:
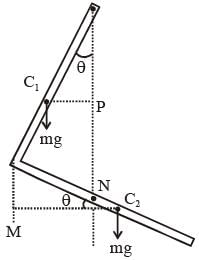
An L-shaped object, made of thin rods of uniform mass density, is suspended with a string as shown in figure. If AB = BC, and the angle made by AB with downward vertical is θ, then :
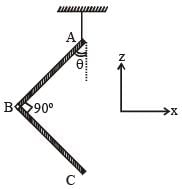
A mixture of 2 moles of helium gas (atomic mass = 4 u), and 1 mole of argon gas (atomic mass = 40 u) is kept at 300 K in a container. The ratio of their rms speeds 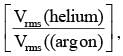 is close to
is close to
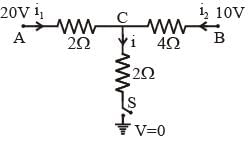
When the switch S, in the circuit shown, is closed, then the value of current i will be :
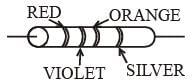
A resistance is shown in the figure. Its value and tolerance are given respectively by:
A bar magnet is demagnetized by inserting it inside a solenoid of length 0.2 m, 100 turns, and carrying a current of 5.2 A. The coercivity of the bar magnet is :
A rod, of length L at room temperature and uniform area of cross section A, is made of a metal having coefficient of linear expansion α/ °C. It is observed that an external compressive force F, is applied on each of its ends, prevents any change in the length of the rod, when its temperature rises by ΔT K. Young's modulus, Y, for this metal is :
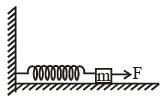
A block of mass m, lying on a smooth horizontal surface, is attached to a spring (of negligible mass) of spring constant k. The other end of the spring is fixed, as shown in the figure. The block is initally at rest in its equilibrium position. If now the block is pulled with a constant force F, the maximum speed of the block is :
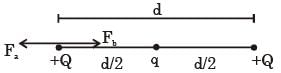
Three charges +Q, q, + Q are placed respectively, at distance, 0, d/2 and d from the origin, on the x-axis. If the net force experienced by + Q, placed at x= 0, is zero, then value of q is :
A conducting circular loop made of a thill wire, has area 3.5 x 10-3 m2 and resistance 10Ω . It is placed perpendicular to a time dependent magnetic field B(t) = (0.4T)sin(50πt). The field is uniform in space. Then the net charge flowing through the loop during t = 0 s and t = 10 ms is close to:
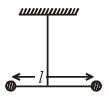
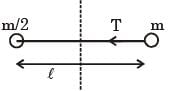
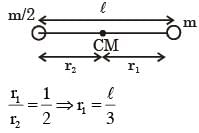
Two masses m and m/2 are connected at the two ends of a massless rigid rod of length l.The rod is suspended by a thin wire of torsional constant k at the centre of mass of the rod-mass system(see figure). Because of torsional constant k, the restoring torque is π=kθ for angular displacement 0. If the rod is rotated by θ0 and released, the tension in it when it passes through its mean position will be.
A copper wire is stretched to make it 0.5% longer. The percentage change in its electrical resistance if its volume remains unchanged is:
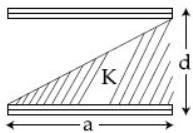
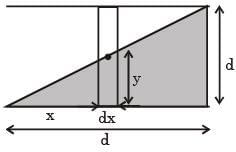
A parallel plate capacitor is made of two square plates of side 'a', separated by a distance d (d<<a). The lower triangular portion is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant K, as shown in the figure. Capacitance of this capacitor is :
Mobility of electrons in a semiconductor is defined as the ratio of their drift velocity to the applied electric field. If, for an n-type semiconductor, the density of electrons is 1019m-3 and their mobility is 1.6 m2/(V.s) then the resistivity of the semiconductor (since it is an n-type semiconductor contribution of holes is ignored) is close to:
If the angular momentum of a planet of mass m, moving around the Sun in a circular orbit is L, about the center of the Sun, its areal velocity is :
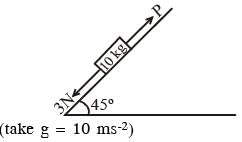
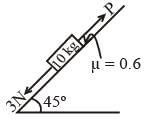
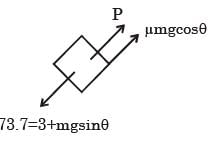
A block of mass 10 kg is kept on a rough inclined plane as shown in the figure. A force of 3 N is applied on the block. The coefficient of static friction between the plane and the block is 0.6. What should be the minimum value of force P, such that the block doesnot move downward ?
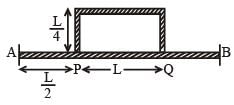
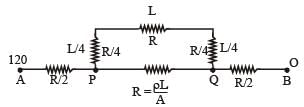
Temperature difference of 120°C is maintained between two ends of a uniform rod AB of length 2L. Another bent rod PQ, of same cross- section as AB and length 3L/2 is connected across AB (See figure). In steady state, temperature difference between P and Q will be close to :
A heavy ball of mass M is suspended from the ceiling of a car by a light string of mass m (m<<M). When the car is at rest, the speed of transverse waves in the string is 60 ms-1. When the car has acceleration a, the wave-speed increases to 60.5 ms-1. The value of a, in terms of gravitational acceleration g, is closest to :
A sample of radioactive material A, that has an activity of 10 mCi(1 Ci = 3.7 x 1010 decays/s), has twice the number of nuclei as another sample of a different radioactive material B which has an activity of 20 mCi. The correct choices for half-lives of A and B would then be respectively :
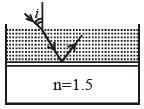
Consider a tank made of glass(reiractive index 1.5) with a thick bottom. It is filled with a liquid of refractive index μ. A student finds that, irrespective of what the incident angle i (see figure) is for a beam of light entering the liquid, the light reflected from the liquid glass interface is never completely polarized. For this to happen, the minimum value of μ is :
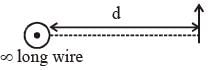
An infinitely long current carrying wire and a small current carrying loop are in the plane of the paper as shown. The radius of the loop is a and distance of its centre from the wire is d (d»a). If the loop applies a force F on the wire then :
Surface of certain metal is first illuminated with light of wavelength λ1 =350 nm and then, by light of wavelength λ2=540 nm. It is found that the maximum speed of the photo electrons in the two cases differ by a factor of 2. The work function of the metal (in eV) is close to :
(Energy of photon = 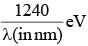 )
)
A particle is moving with a velocity 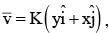 where K is a constant. The general equation for its path is:
where K is a constant. The general equation for its path is:
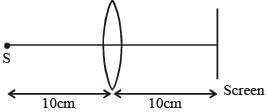
A convex lens is put 10 cm from a light source and it makes a sharp image on a screen, kept 10 cm from the lens. Now a glass block (refractive index 1.5) of 1.5 cm thickness is placed in contact with the light source. To get the sharp image again, the screen is shifted by a distance d. Then d is :
For a uniformly charged ring of radius R, the electric field on its axis has the largest magnitude at a distance h from its centre. Then value of h is :
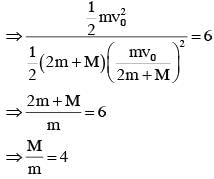
Three blocks A, B and C are lying on a smooth horizontal surface, as shown in the figure. A and B have equal masses, m while C has mass M. Block A is given an brutal speed v towards B due to which it collides with B perfectly inelastically. The combined mass collides with C, also perfectly inelastically 5/6 th of the initial kinetic energy is lost in whole process. What is value of M/m ?
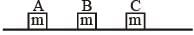
Drift speed of electrons, when 1.5 A of current flows in a copper wire of cross section 5 mm2, is v. If the electron density in copper is 9 ×1028 /m3 the value of v in mm/s is close to (Take charge of electron to be =1.6 × 10–19C)


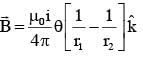
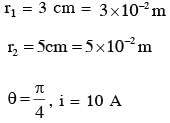
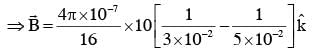
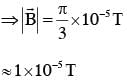
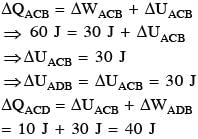

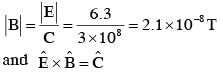
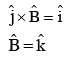
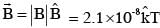
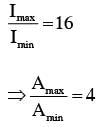
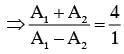
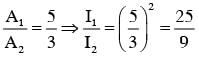
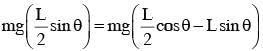
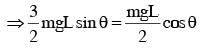
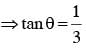
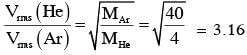
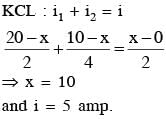
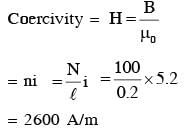

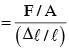
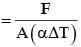
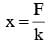
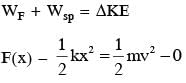
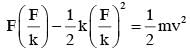
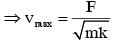
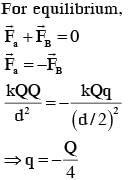
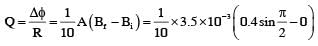
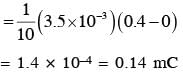
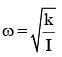
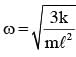
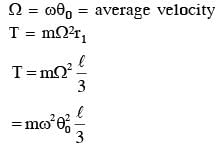
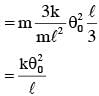
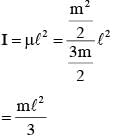
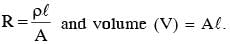
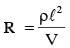
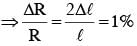
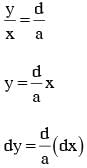
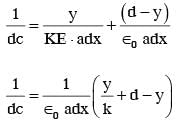
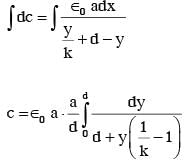
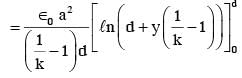
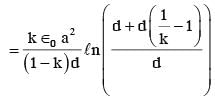
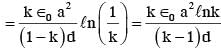
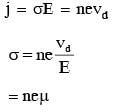
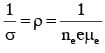

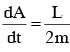
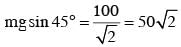
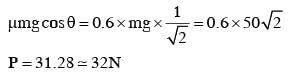
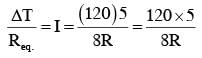
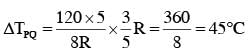
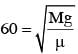
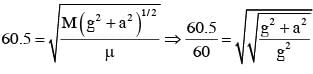
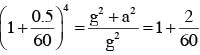
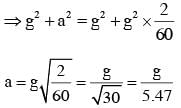
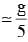
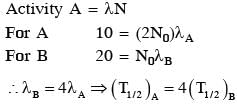
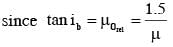
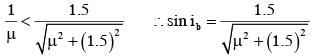
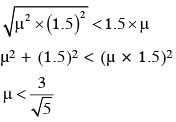
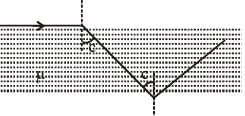
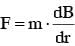
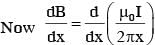
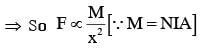
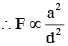
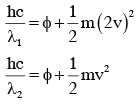
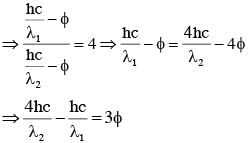
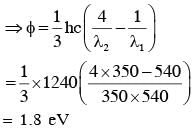
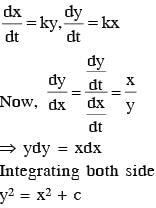
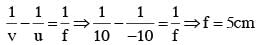
 in the direction of incident ray
in the direction of incident ray