BITSAT Practice Test - 6 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test BITSAT Mock Tests Series & Past Year Papers 2025 - BITSAT Practice Test - 6
Two bars of thermal conductivities K and 3K and lengths 1 cm and 2 cm, respectively, have equal cross-sectional area, they are joined lengthwise as shown in the figure. If the temperature at the ends of this composite bar is 0°C and 100°C respectively (see figure), then the temperature (T) of the interface is:


As the temperature of a liquid is raised, the coefficient of viscosity,
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Assertion: Gravitational force on an object on the moon is one-sixth that on the earth.
Reason: The law of gravitation is the same on both the moon and the earth.
A particle of mass m moving with a velocity v strikes a wall and rebounds back. If the magnitude of the velocity is unchanged, the magnitude of force exerted on the wall by the particle during the time of contact, t will be -
A generator has an e.m.f. of 440 V and internal resistance of 400 Ω. Its terminals are connected to a load of 4000 ohm. The voltage across the load is
Assertion: Threshold wavelength of certain metal λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on the plate. It is found that after some time the emission of electrons stops
Reason: The ejected electrons experience force of attraction due to development of positive charges on plate which after certain time is adequate enough to hold them to plate itself.
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror, at a distance of 15 cm from the pole. The radius of curvature of the mirror is 20 cm and the object is made to oscillate along the principal axis with an amplitude of 2 mm. The amplitude of its image will be
At a certain instant a stationary transverse wave is found to have maximum kinetic energy. The appearance of string at that instant is
A bird is sitting in a large closed cage which is placed on a spring balance. It records a weight of 25 N. The bird (mass m = 0.5 kg) flies upward in the cage with an acceleration of 2 ms−2. The spring balance will now record a weight of
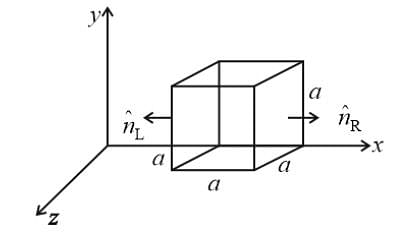
The electric field components in the given figure are Ex = αx1/2 and Ey = Ez = 0 in which α = 800 N C−1 m−1/2. The charge within the cube is, if net flux through the cube is 1.05 m2 C−1 (assume a = 0.1 ma = 0.1 m)
Two blocks of masses M and m are connected by a string passing over a pulley as shown in the figure.

The downward acceleration of the block with mass m is
For a given velocity, a projectile has the same range R for two angles of projection. If t1 and t2 are the times of flight in the two cases, then:
A block is kept on a frictionless inclined surface with angle of inclination α. The incline is given an acceleration 'a' to keep the block stationary. Then 'a' is equal to
A particle of mass m moves on the x-axis under the influence of a force of attraction towards the origin O, given by  . If it starts from rest at a distance 'a' from the origin, the speed attained by it after reaching a point at a distance x will be
. If it starts from rest at a distance 'a' from the origin, the speed attained by it after reaching a point at a distance x will be
A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R rolls down an inclined plane of height 'h'. The angular velocity of the cylinder when it reaches the bottom of the plane will be
Suppose the gravitational force varies inversely as the nth power of the distance. The time period of a planet in circular orbit of radius R around sun will be proportional to:
Directions: In the following question, Statement-1 (Assertion) is followed by Statement-2 (Reason). The question has the following four choices out of which only one choice is correct.
Statement-1: The critical velocity of a liquid flowing through a tube is inversely proportional to the radius of the tube.
Statement-2: The velocity of a liquid flowing through a tube is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the tube.
Directions: The air column in a pipe closed at one end is made to vibrate in its second overtone by a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 320 ms-1. The end correction may be neglected. Let P0 denote the mean pressure at any point in the pipe and ΔP0 denote the maximum amplitude of pressure variation.
The length L of the air column is
A carnot engine has efficiency 1/5. Efficiency becomes 1/3 when temperature of sin k is decreased by 50 K. What is the temperature of source?
When the potential function at any point is given by the expression , the magnitude of the electric field at any point is given by
An electron is accelerated to a high speed down the axis of a cathode ray tube by the application of a potential difference of V volts between the cathode and the anode. The particle then passes through a uniform transverse magnetic field in which it experiences a force F. If the potential difference between the anode and the cathode is increased to 2 V, the electron will now experience a force of
The number of turns and the radius of cross-section of the coil of a tangent galvanometer are doubled. The value of the reduction factor k will be
In an inductor, the current I (in amperes) varies with time t (in seconds) as I = 5 + 16t. If the emf induced in the inductor is 10 mV, then the power supplied to the inductor at t = 1s is
A thin equi-convex lens is made of glass with refractive index 1.5, and its focal length is 0.2 m. If it acts as a concave lens of 0.5 m focal length when dipped in a liquid, the refractive index of the liquid is:
Assume that the nuclear binding energy per nucleon (B/A) versus mass number (A) is as shown in the figure below. Use this plot to choose the correct choice.
A transistor is used as an amplifier in CB mode with a load resistance of 5 kW. The current gain of the amplifier is 0.98 and the input resistance is 70 W. The voltage gain and power gain respectively, are
|
2 videos|17 docs|85 tests
|
|
2 videos|17 docs|85 tests
|





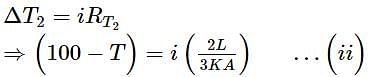




 has finite values and is defined for all values of t.
has finite values and is defined for all values of t.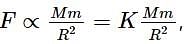

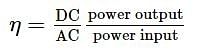


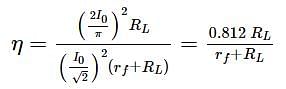


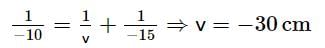
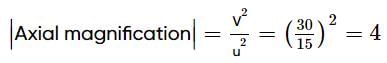
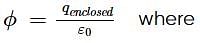




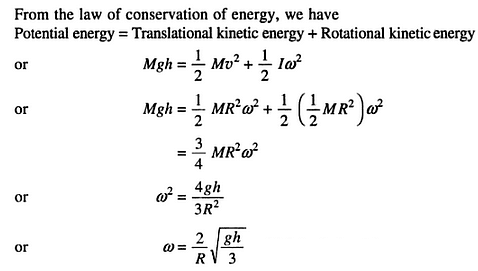








 = 1.0 m
= 1.0 m
 = k
= k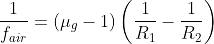 ...(i)
...(i) ... (ii)
... (ii) ...(iii)
...(iii)
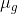 = 1.5
= 1.5 = ?
= ?




















