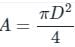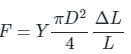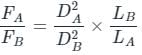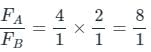31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Mechanical Properties of Solids - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 11 - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Mechanical Properties of Solids
Two wires A and B are of the same material. Their lengths are in the ratio 1 : 2 and the diameter are in the ratio 2 : 1. If they are pulled by the same force, then increase in length will be in the ratio
When an elastic material with Young’s modulus Y is subjected to stretching stress S, elastic energy stored per unit volume of the material is
The following four wires are made of the same material. Which of these will have the largest extension when the same tension is applied ?
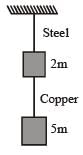
If the ratio of diameters, lengths and Young’s modulus of steel and copper wires shown in the figure are p, q and s respectively, then the corresponding ratio of increase in their lengths would be [2013]
The stress-strain curves are drawn for two different materials X and Y. It is observed that the ultimate strength point and the fracture point are close to each other for material X but are far apart for material Y. We can say that materials X and Y are likely to be (respectively)
A wire of length L, area of cross section A is hanging from a fixed support. The length of the wire changes to L1 when mass M is suspended from its free end. The expression for Young’s modulus is
When a block of mass M is suspended by a long wireof length L, the length of the wire becomes (L + l).The elastic potential energy stored in the extended wire is
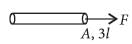
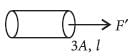
Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume. The first wire has cross-sectional area A and the second wire has cross-sectional area 3A. If the length of the first wire is increased by Dl on applying a force F, how much force is needed to stretch the second wire by the same amount?
The bulk modulus of a spherical object is ‘B’. If it is subjected to uniform pressure ‘p’, the fractional decrease in radius is
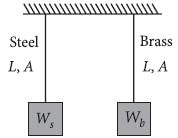
The Young’s modulus of steel is twice that of brass. Two wires of same length and of same area of cross section, one of steel and another of brass are suspended from the same roof. If we want the lower ends of the wires to be at the same level, then the weights added to the steel and brass wires must be in the ratio of
The approximate depth of an ocean is 2700 m. The compressibility of water is 45.4 × 10–11 Pa–1 and density of water is 103 kg/m3. What fractional compression of water will be obtained at the bottom of the ocean?
Copper of fixed volume V is drawn into wire of length l. When this wire is subjected to a constant force F, the extension produced in the wire is Dl. Which of the following graphs is a straight line?
The following four wires are made of the same material. Which of these will have the largest extension when the same tension is applied?
If the ratio of diameters, lengths and Young’s modulus of steel and copper wires shown in the figure are p, q and s respectively, then the corresponding ratio of increase in their lengths would be
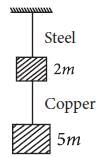
Two wires A and B are of the same materials. Their lengths are in the ratio 1:2 and the diameters are in the ratio 2:1. When stretched by force FA and FB respectively they get equal increase in their lengths. Then the ratio FA/FB should be:
|
119 videos|491 docs|98 tests
|


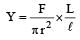
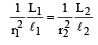
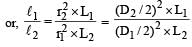
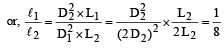
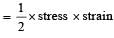
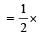 stress (stress / Young' s modulus)
stress (stress / Young' s modulus)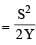

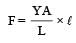
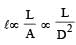
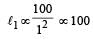
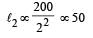
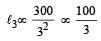
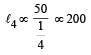
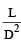 is maximum for case (d).
is maximum for case (d).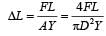
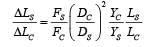
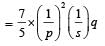
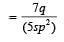
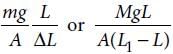
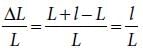
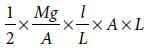
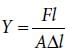

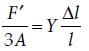

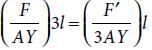

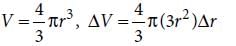
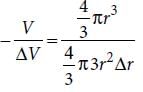
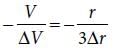
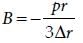
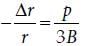

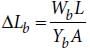
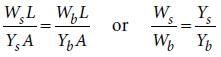
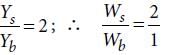
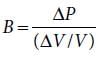
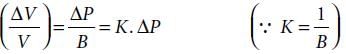
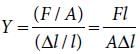
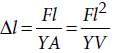 (Using (i))
(Using (i))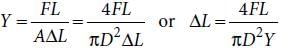
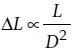
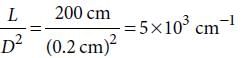
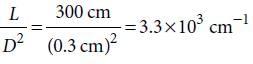
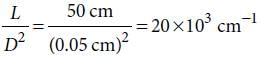
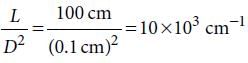
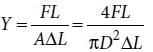
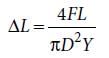
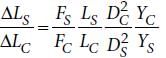
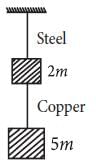
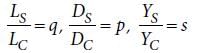
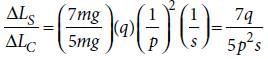
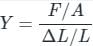 , where
, where