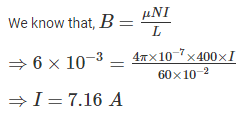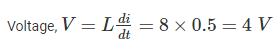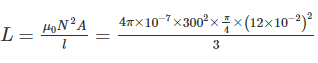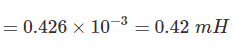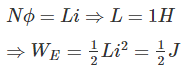Test: Electromagnetic Fields Theory- 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test SSC JE Electrical Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Electromagnetic Fields Theory- 1
A perfect magnetic conductor is defined to be a material for which...
For making a capacitor, it is better to select a dielectric having
Determine the reluctance (in Amp-turns/Wb) of a coil, when the flux through the coil is 25 Wb and the value of produced mmf is 50 Amp-turns
Determine the current (in A) through a 60 cm long solenoid when the solenoid has 400 turns and the value of magnetic field at the centre of the solenoid is 6 mT.
When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, the field strength _____.
Which one of the following materials cannot be used for permanent magnets?
A conductor of length 0.6 m is situated at the right angle to a uniform magnetic field of flux density 4 Wb/sq. m. The conductor is moving with a velocity of 50 m/s. Calculate the emf induced (in V) n the conductor.
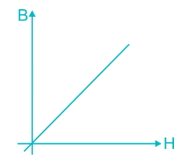
The graph shown below represents the B-H curve for _______
If the magnetic susceptibility of any material is less than zero then the material is ________.
Which one of the following is the CORRECT expression for magnetic susceptibility?
What will be the voltage (in V) across a 8 H inductor, when the rate of change of current in the inductor is 0.5 A/sec.
Determine the intensity of magnetization (in A/m) of a magnet when the pole strength of the magnet is 30 A-m and the area of the pole of the magnet is 2 sq. m.
Which property of a material opposes the passage of magnetic flux through it?
Determine the self-inductance (in mH) of a 3 m long air-cored solenoid, when the coil has 300 turns and the diameter of the coil 12 cm.
Midway between two equal and similar charges, a third equal and similar charge is placed. Then this third charge will ________.
Which law states that “the line integral of the magnetic field intensity H around a closed path is equal to the total current linked by the contour”?
A coil of 1000 turns is wound on a core. A current of 1 A flowing through the coil creates a core flux of 1 mWb. What is the energy stored in the magnetic field?
Which one of the following is the CORRECT value of magnetic permeability in free space?
|
2 videos|1 docs|55 tests
|



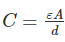 hence with dielectric having high permittivity higher values of capacitance can be achieved with small capacitor size.
hence with dielectric having high permittivity higher values of capacitance can be achieved with small capacitor size.