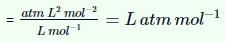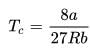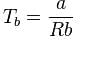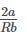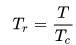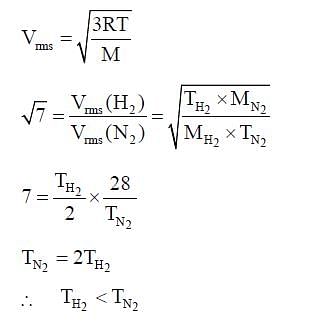IIT JAM Chemistry - MCQ Test 1 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry - IIT JAM Chemistry - MCQ Test 1
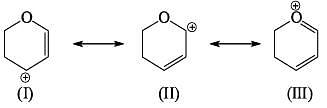
The most stable canonical structure among all of above is:

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Compare relative stability of the following structures:


Strength of following bases decrease in the order?
(I) Br- (II) F- (III) NH2 (IV) CH3-
The ratio of van der Waal’s constant a and b, 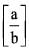 has the dimensions of:
has the dimensions of:
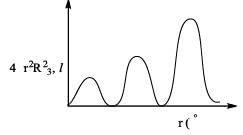
Find the corresponding subshell utilizing the information from graph.
Distribution of molecules with velocity is represented by curve as shown:
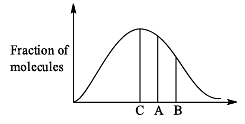
Velocity at point A is:
Of the following acids, the one that is strongest is:
Lattice energy (numerical value) of chloride of alkali metals is in order:
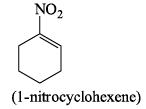
Which of the following drawings is not a resonance structure of 1 -nitrocyclohexene:
Which of the following is not resonating structure of each other?
Examine the following resonating structures of formic acid for their individual stability and then answer the question given below:


Which of the following arrangements gives the correct order of decreasing stability of the above-mentioned resonance contributors?
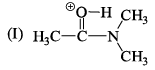
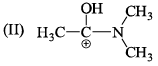
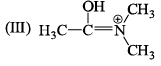
The correct stability order of the given resonating structures is:
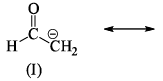
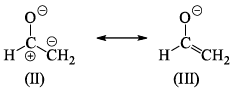
The correct order of stability for the given canonical structures is:
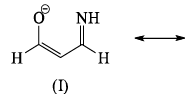
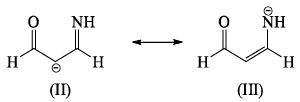
The correct order of stability among the following canonical structure is:
If a particle in the box of length 'l' has wavelength, ψ = (l -x)x. (x is only variable) What is its normalization constant?
Match column I with column II and select the correct answers:



The table indicates the value of van-der Waal’s constant ‘a’. The gas which can be liquefied most easily is:
rms velocity of hydrogen is √7 times the rms velocity of nitrogen. If T is the temperature of gas,then:
Copper containing alloy weighing 0.3175g dissolved in an acid, and an excess of KI is added.
Estimation of copper in alloy is based on following reactions:
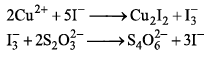
If a particle has linear momentum 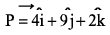 at position
at position 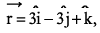 , then its angular momentum is:
, then its angular momentum is:
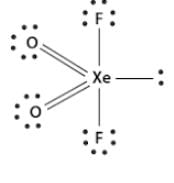
Consider two molecules A & B.

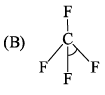
∠α = ∠HCH; ∠β = ∠FCF
Which of following is true?
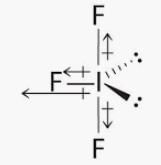
Predict the shape of IF4+ molecule using VSEPR theory:
Which of the following is true for ionization energy:
What is the correct increasing order of bond lengths of bond indicated in following compund?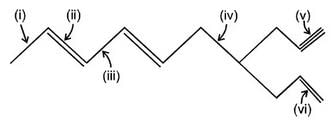
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their bond angles: NH3, H2O , CH4
The ground state electronic configuration of valence shell electrons in a molecule A2 is written as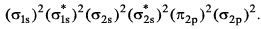 • Hence bond order is_____________________.
• Hence bond order is_____________________.
|
2 docs|25 tests
|