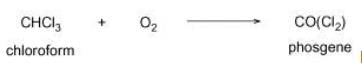Morrison & Boyd Test: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Morrison & Boyd Test: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes
Alkyl halides are insoluble in water
The most common freons in industrial use is manufactured by
The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is by treating the alcohol with
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as main product
Dichloromethane (Methylene chloride) is
Which one of the following forms propanenitrile as the major product?
Bromomethane, Chloromethane, Dibromomethane, 1 – Chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1 – Chlorobutaneare all
In the reaction, R – X + NaOR’ → ROR’ + X (– ve ion). The main product formed is
Hydrocarbons are prepared from Grignard reagent by
Which one of the following is employed as antityphoid drug?
CH3=CH2CH3 + H – I → CH3CH2CH2I + CH3CHICH3 (major). This reaction is
Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous conditions because
If ‘n’ represents total number of asymmetric carbon atoms in a compound, the possible number of optical isomers of the compound is
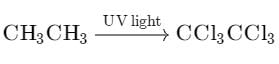
Chlorination of ethane is carried out in presence of
Which one of the following is a synthetic halogen compound?
Name the following aryl halide as per the IUPAC system
Carbon tetra chloride has a dipole moment_____.
Decreasing order of reactivity of hydrogen halide acids in the conversion of ROH →RX is
Chlorination of ethane is carried out in presence of
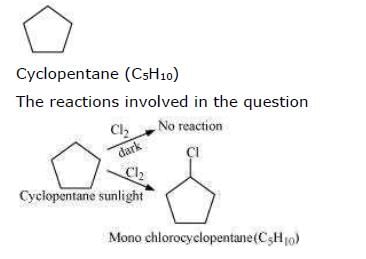
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. The hydrocarbon is
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged because
Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide?
Methyl bromide is converted into ethane by heating it in ether medium with
p – Dichlorobenzene has than those of o – and m – isomers
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|