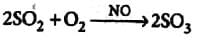NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Chemistry Class 12 > Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT)
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) for NEET 2024 is part of Chemistry Class 12 preparation. The Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) questions and answers have been
prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) MCQs are made for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) below.
Solutions of Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry Class 12 for NEET & Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry Class 12 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry Class 12 for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 1
Which of the following statements is correct about solid catalysts?
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 1
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 2
Which of the following can adsorb larger volume of hydrogen gas?
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 3
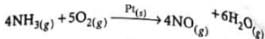
Traces of molybdenum are used with finely divided iron which acts as a catalyst during Haber’s process for synthesis of ammonia. The molybdenum
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 3
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 4
Which kind of catalysis can be explained on the basis of adsorption theory?
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 4
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 5
According to adsorption theory of catalysis, the rate of reaction increases with the use of a catalyst because
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 5
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 6
The oxide of nitrogen which acts as a catalyst in lead chamber process is
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 6
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 7
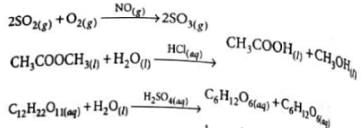
Which of the following is an example of heterogeneous catalysis?
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 8
Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 9
Which of the following statements about zeolites is not correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) - Question 10
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
Information about Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Catalysis (Old NCERT), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice