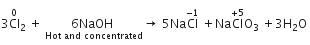Test: General Properties of Group-17 (Halogens) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: General Properties of Group-17 (Halogens)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following property decreases down the group in the halogens?
Which of the following represents the decreasing order of van der Waals’ forces in halogens ?
The correct order of in creasing order of radiiions Br- , F-, O2- and S2- is as follow
The correct order for the percentage of ionic character is
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
Which option is incorrect among the following for the given property?
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from
Which of the following does not exist?
One gas bleaches the colour of flowers by reduction and another gas by oxidation. The gases respectively are
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
The fluoride ores are
Which one of the following arrangements do not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it?
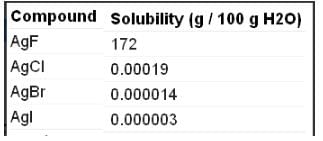
Which of the following are insoluble in water?
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Group 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.
Q. Valence shell configuration that belongs to most reactive non-metal is
Passage
Group 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.
Q.
In which of the following chlorine has different oxidation states?
Direction (Q. No. 18 and 19) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
Direction (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The num ber of lone pair of electrons present on the central iodine in I-3 ion is
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
When carnallite is dissolved in water the number of ions formed are
The number of water insoluble salts among
AgF, AgCI, AgBr, Agl BeF2, CaF2,KF, PbCI2, HgCI2
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : All halogens are coloured.
Statement II : Halogens absorbs part of the light in the visible region.
|
75 videos|338 docs|78 tests
|