NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Chemistry Class 12 > Test: Properties of Alcohols - NEET MCQ
Test: Properties of Alcohols - NEET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Properties of Alcohols
Test: Properties of Alcohols for NEET 2025 is part of Chemistry Class 12 preparation. The Test: Properties of Alcohols questions and answers have been
prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Properties of Alcohols MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Properties of Alcohols below.
Solutions of Test: Properties of Alcohols questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry Class 12 for NEET & Test: Properties of Alcohols solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry Class 12 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Properties of Alcohols | 10 questions in 15 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry Class 12 for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 1
Which of the following reacts with alcohols to form esters besides carboxylic acids?
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 1
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 2
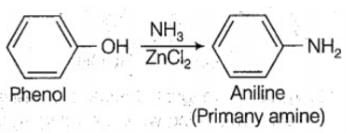
What happens when phenol is treated with ammonia in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl2?
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 2
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 3
When aryl halide is heated with 6-8% NaOH solution ,at 623 K under 300 atm pressure we get:
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 3
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 4
Which alkene is obtained on dehydration of the following alcohol in the presence of H2SO4 ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 4
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 5
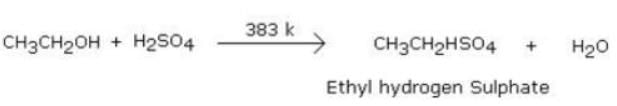
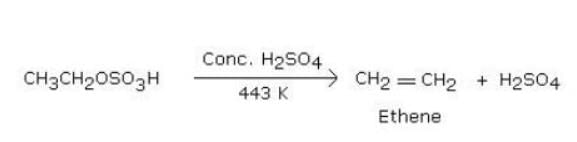
What is the product formed when excess of ethanol reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid at 383 K and then the temperature of reaction mixture is increased to 443 K?
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 5
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 6
Identify the alcohol or phenol from the following which is most soluble in water.
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 8
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 9
Which catalyst is used in Fischer-Speier esterification?
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 9
Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 10
Fermentation of Glucose to alcohol undergoes in presence of :
Detailed Solution for Test: Properties of Alcohols - Question 10
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
Information about Test: Properties of Alcohols Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Properties of Alcohols solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Properties of Alcohols, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice